设计师们最喜欢 UI 工具包,这是一种思路拓展的方法,同时可以利用它们来解决各种复杂的项目,同时可用来了解其他设计师的风格。这里我们收集了最近这一个月一些最棒的 UI 工具包,简介就不再单独翻译。
请观赏:
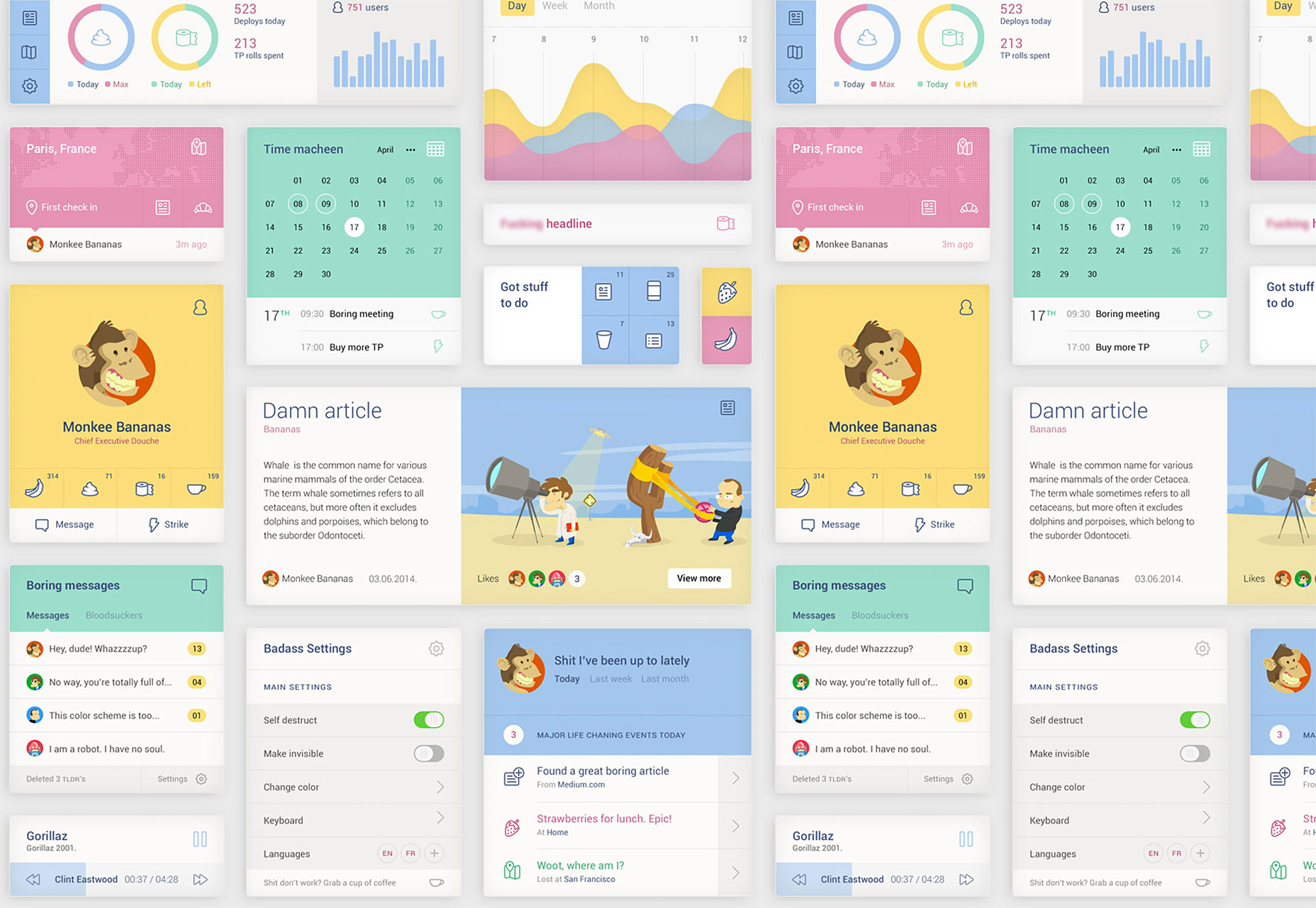
Oh no, not another UI Kit
A great flat UI kit with tons of elements, “Oh no, not another UI Kit” features simple line icons, straitforward layout and a cheeky sense of humor.
Flat UI Kit
A flat UI kit based on Twitter Bootstrap. Supplied in PSD format.

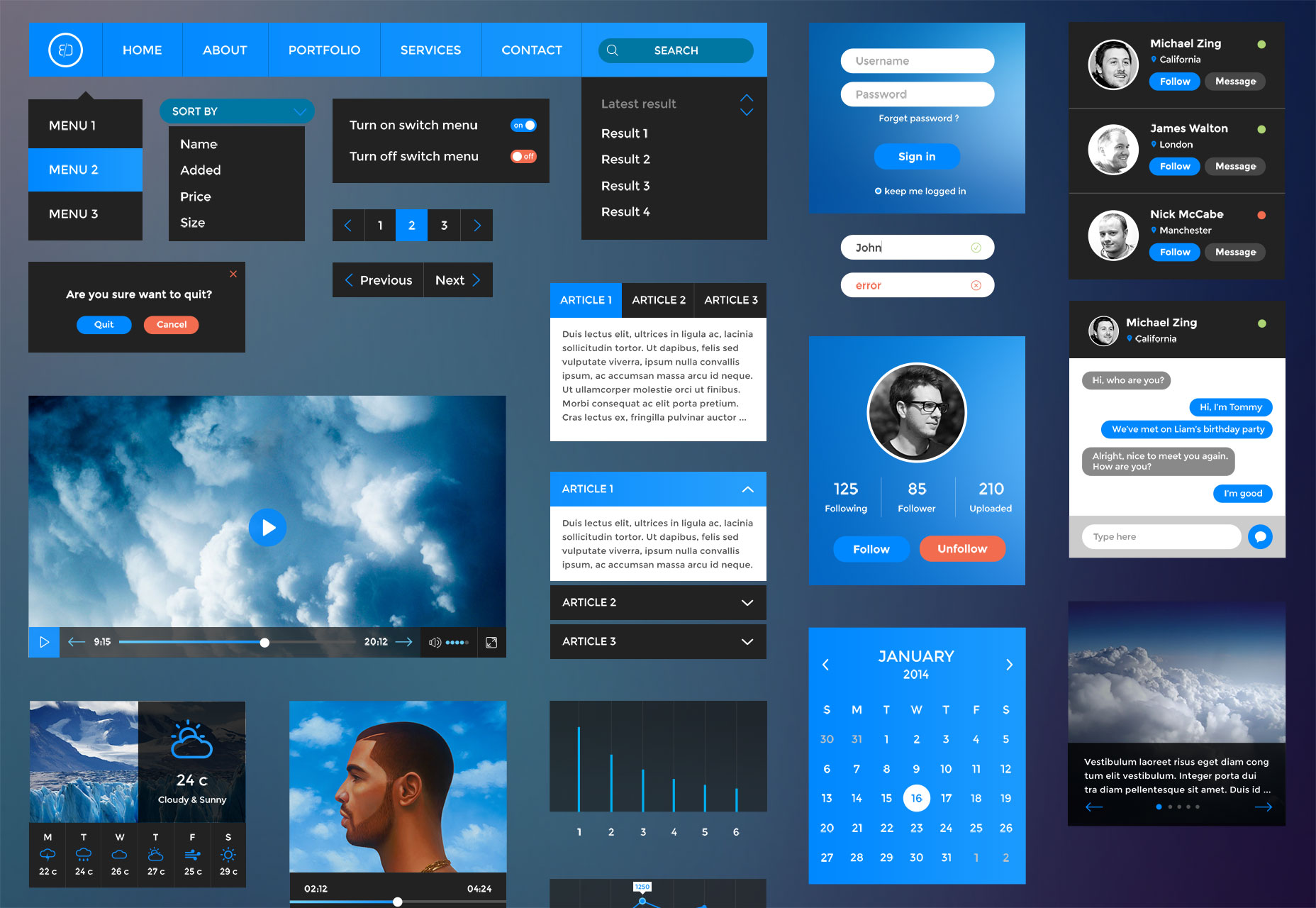
Retina UI web kit
A retina ready UI kit in which dark elements combine with Material Design colors for a powerful effect.
MixKit
A comprehensive UI kit with tons of pop culture colors.
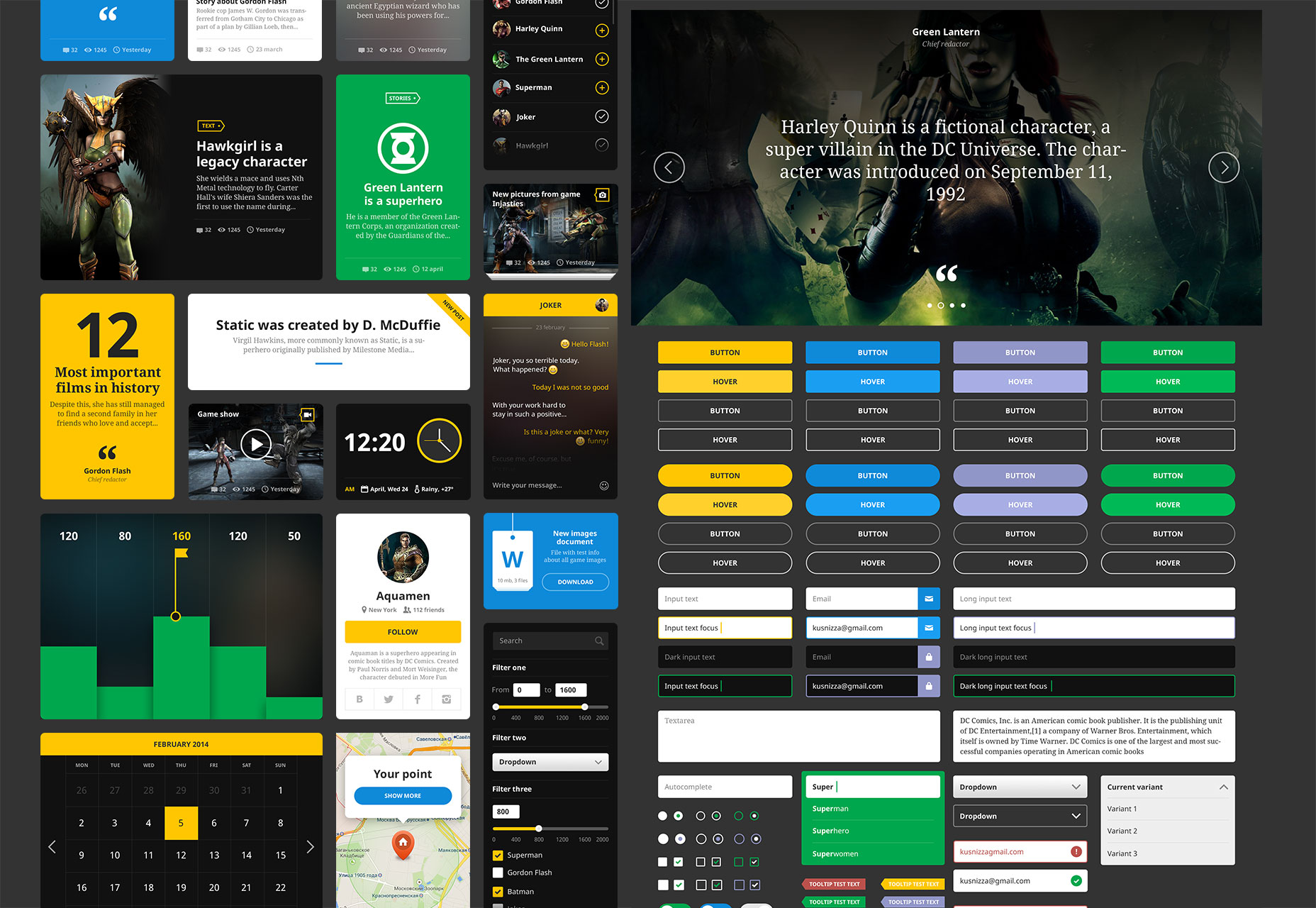
Hero UI
Don’t be fooled by the name, this pseudo-flat UI kit is suitable for any number of projects, although it certainly gives off a comic book vibe.
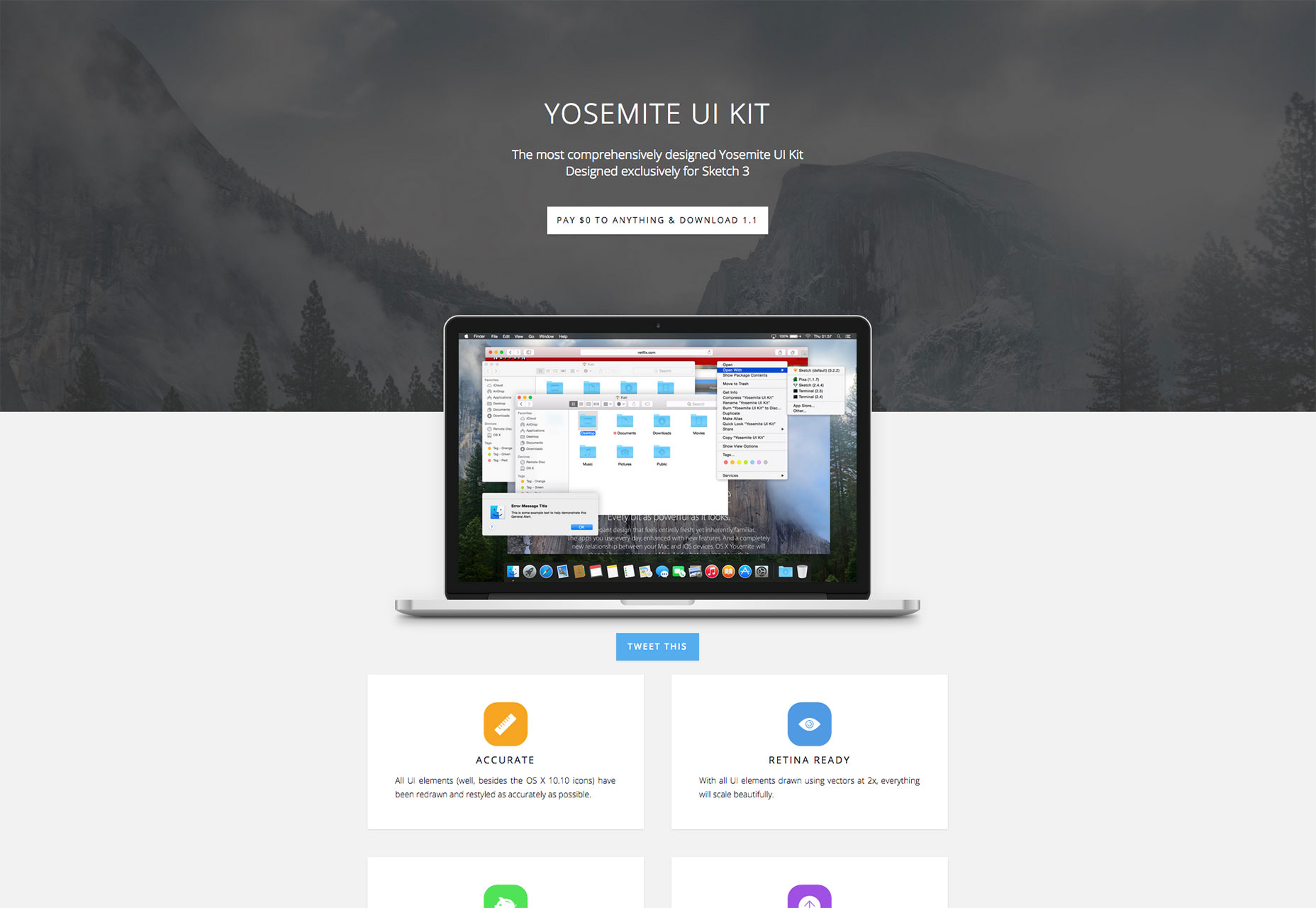
Yosemite UI Kit
Designed exclusively for Sketch 3 this UI kit is perfect for mocking up Mac app screens.
L Bootstrap
This kit features over two dozen different PSDs, in the Android Lollipop style.
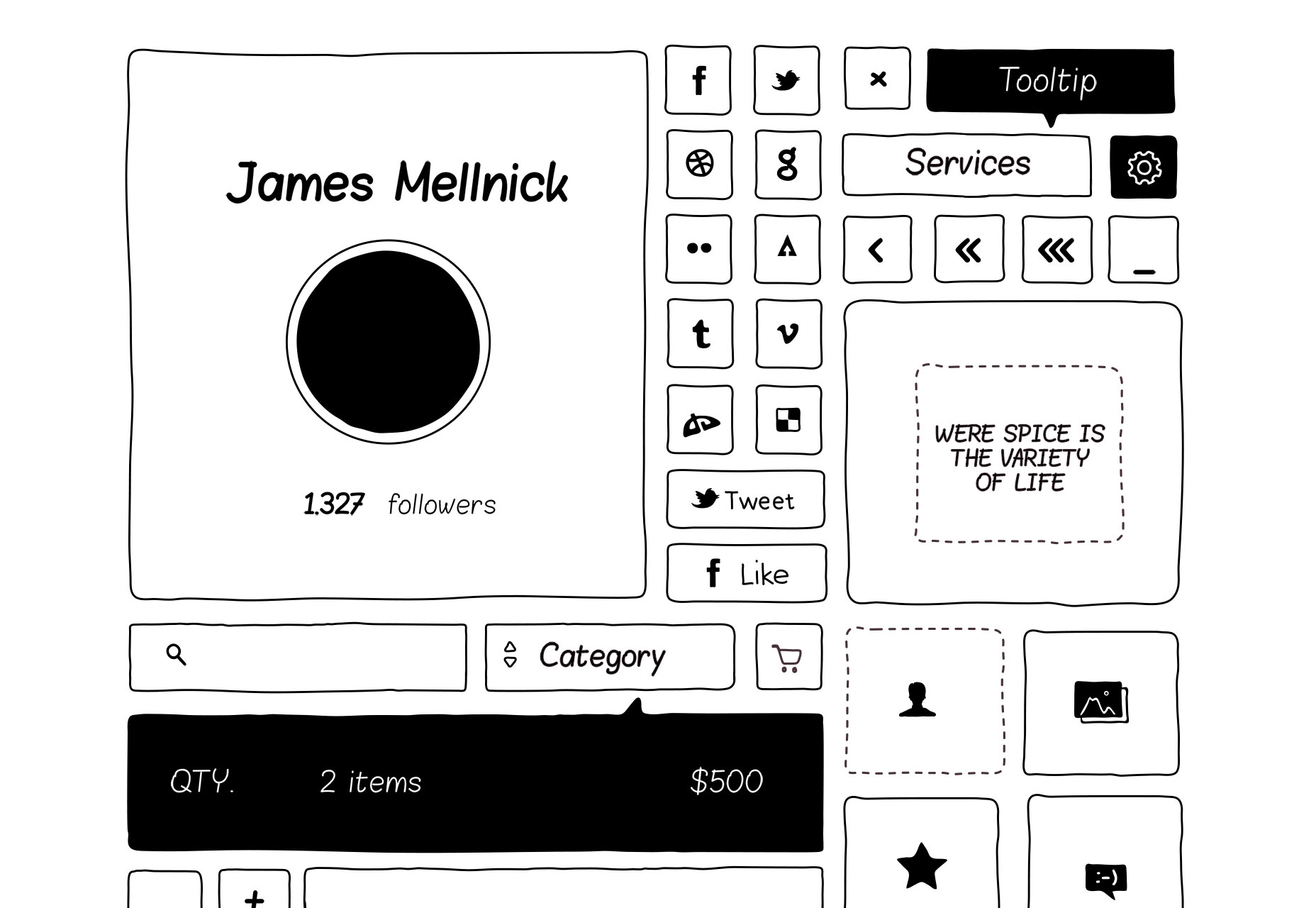
Basiliq
This unique UI kit is designed for prototyping, but will also give your finished designs a lovely hand-drawn feel.
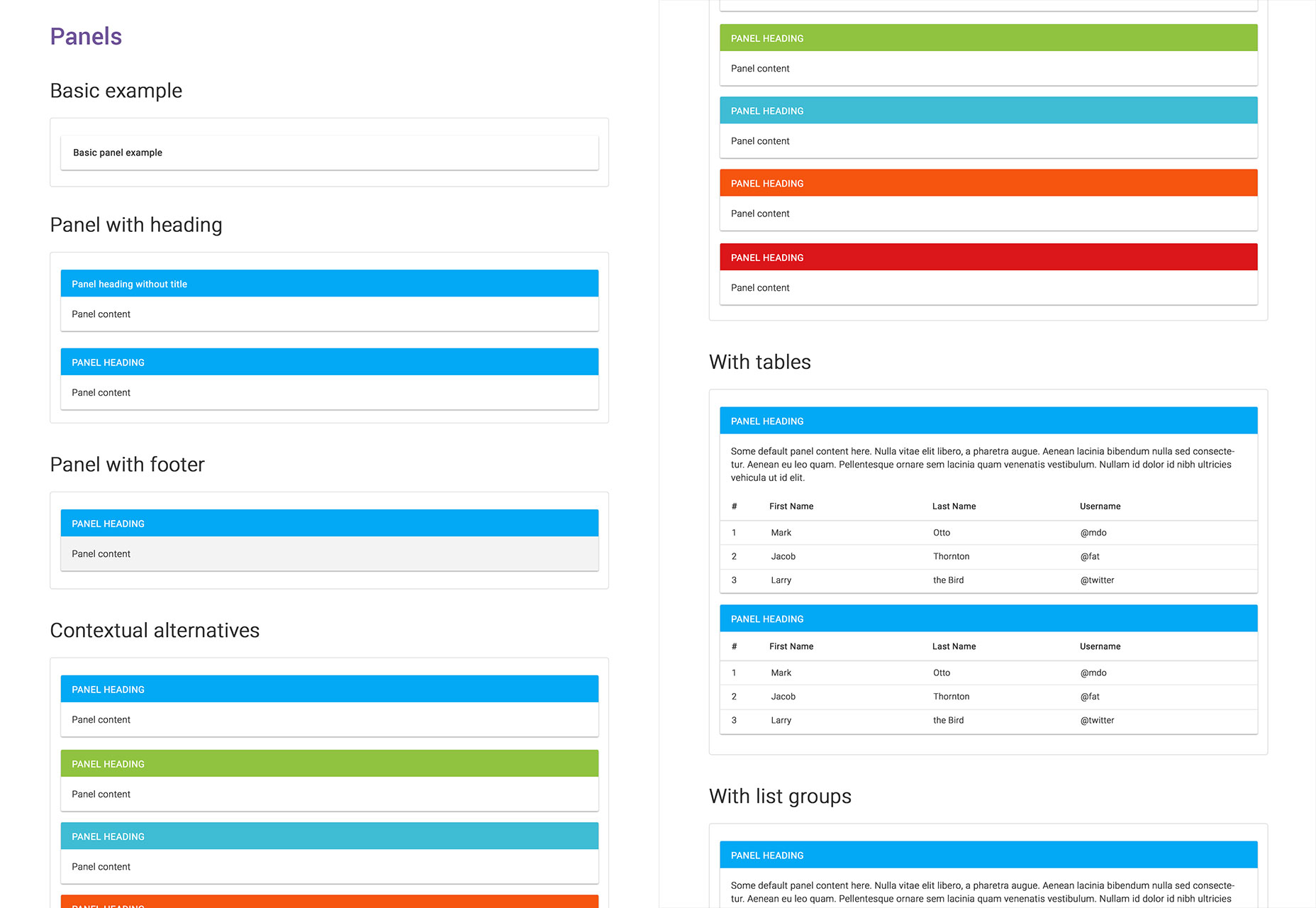
Publica UI Kit
Publica is a comprehensive set of block-style UI elements ideally suited to responsive design.

Mini UI Kit
Designed for Sketch 3, the dark tones in this UI kit add an extra feel of sophistication.

Clino UI Kit
Clino UI Kit is a simple set of UI elements in PSD format, that will suit most modern design projects.
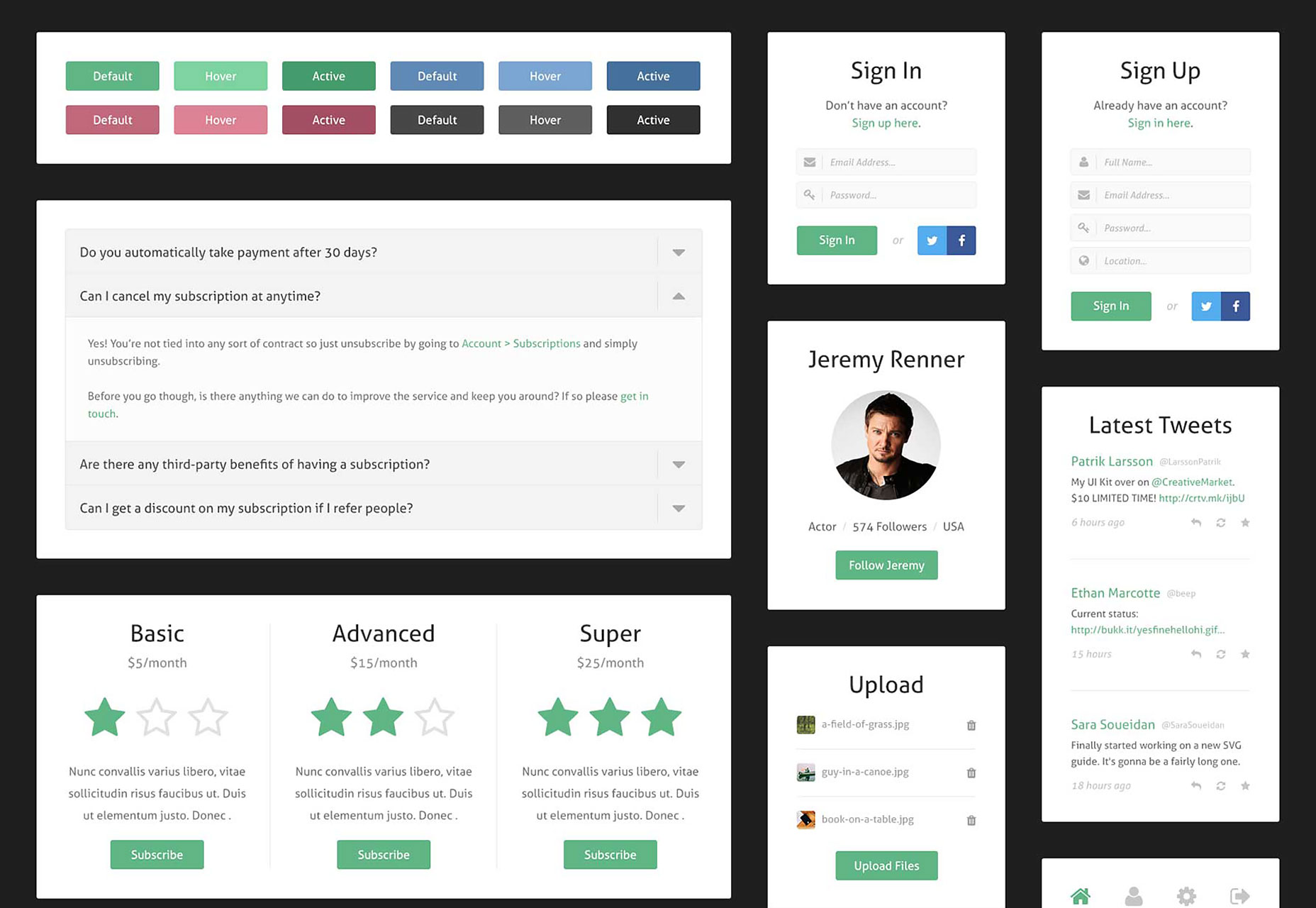
Quadruple Ferial
This UI kit is a perfect blend of minimalism and Google Material Design. It’s ideal for mobile projects.
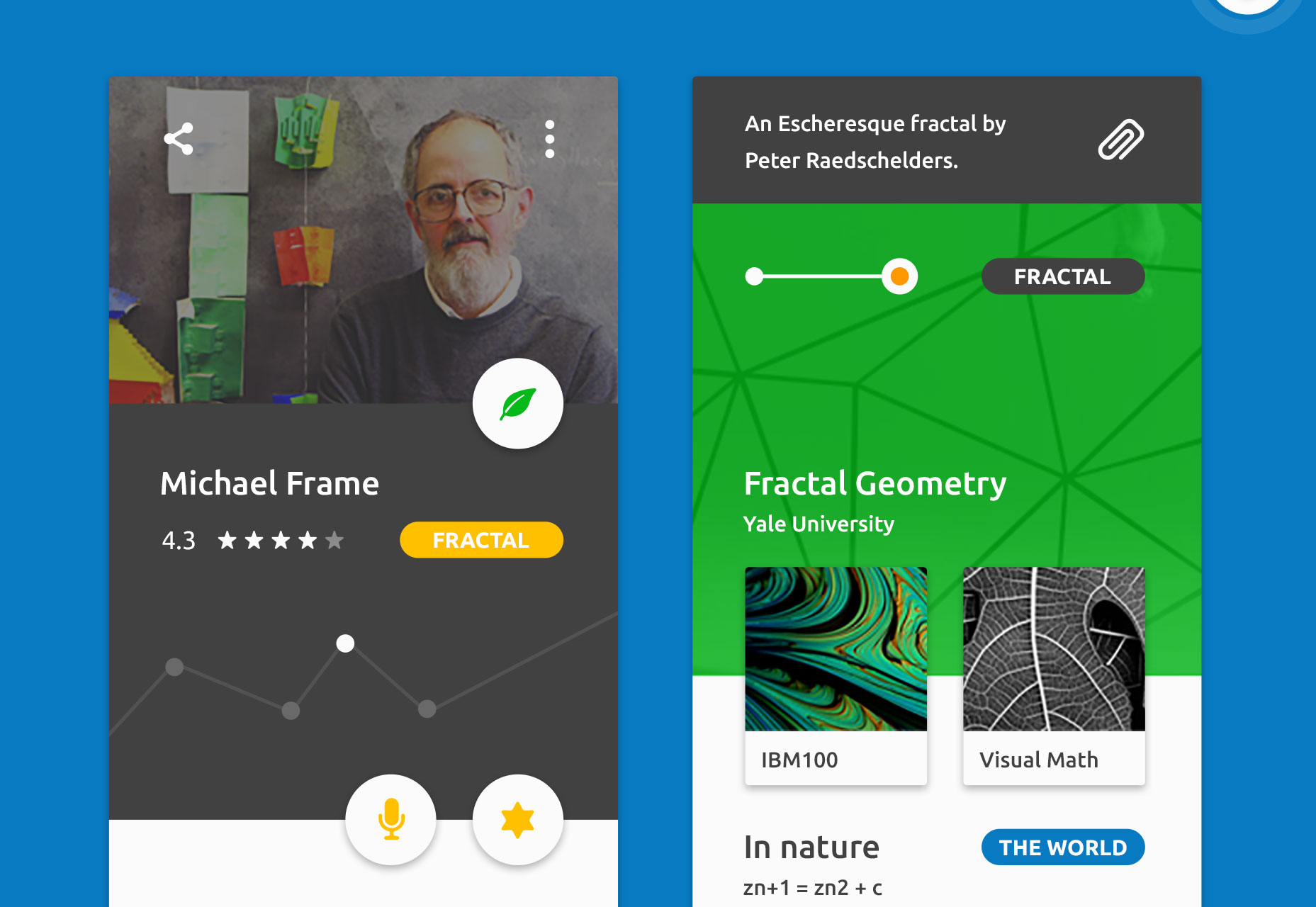
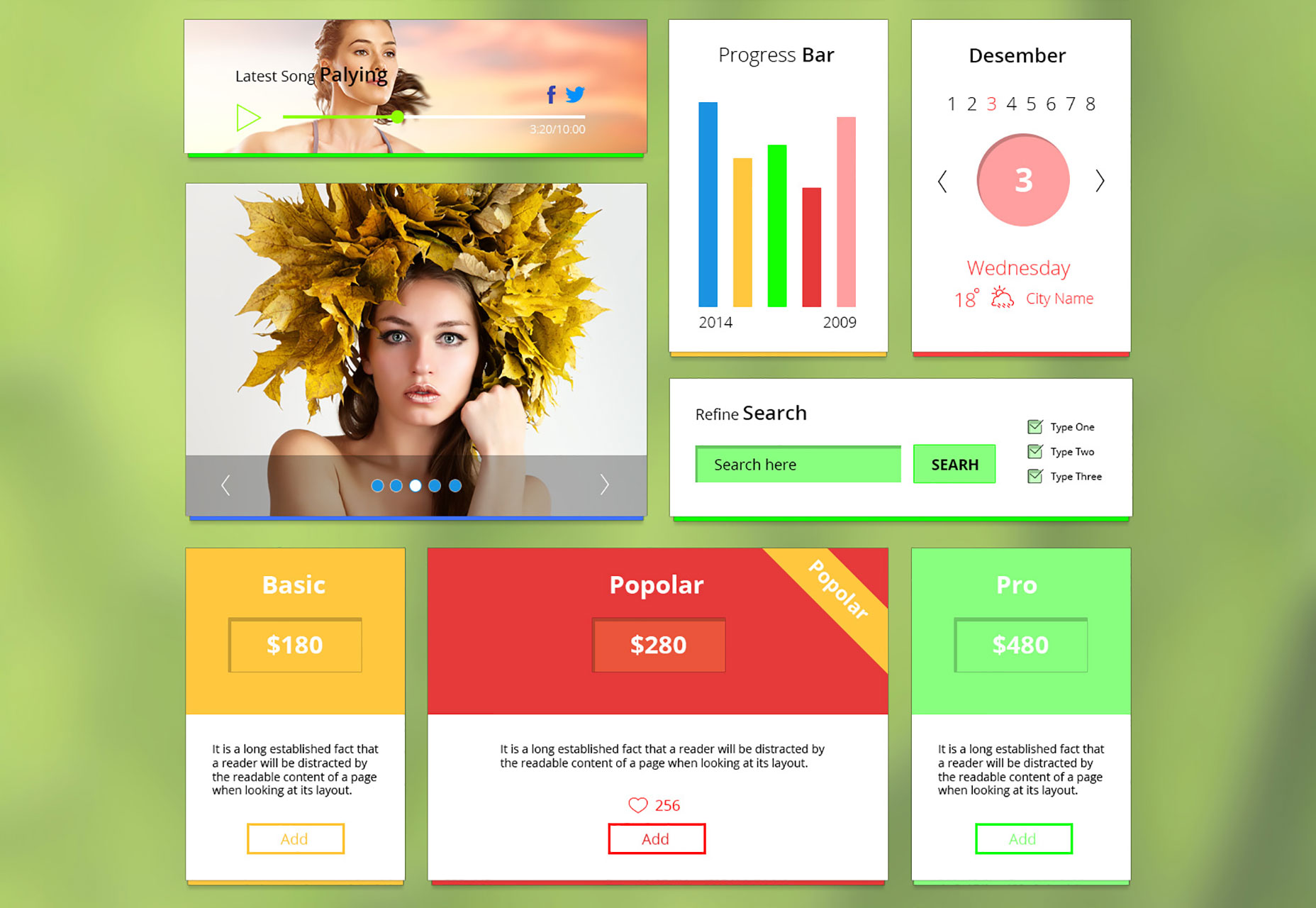
Clean White
This sophisticated and sexy UI kit has more than 55 separate elements and is perfect for all manner of high-end design projects.

Eventray
Eventray is an amazing, comprehensive UI kit that beautifully executes Flat Design.

Number One UI Kit
This sports-based UI kit includes some great specialist UI elements like league tables, and individual sports icons.

Free Minimal UI Kit
This UI kit is based on the Twitter Bootstrap framework and is fully responsive.
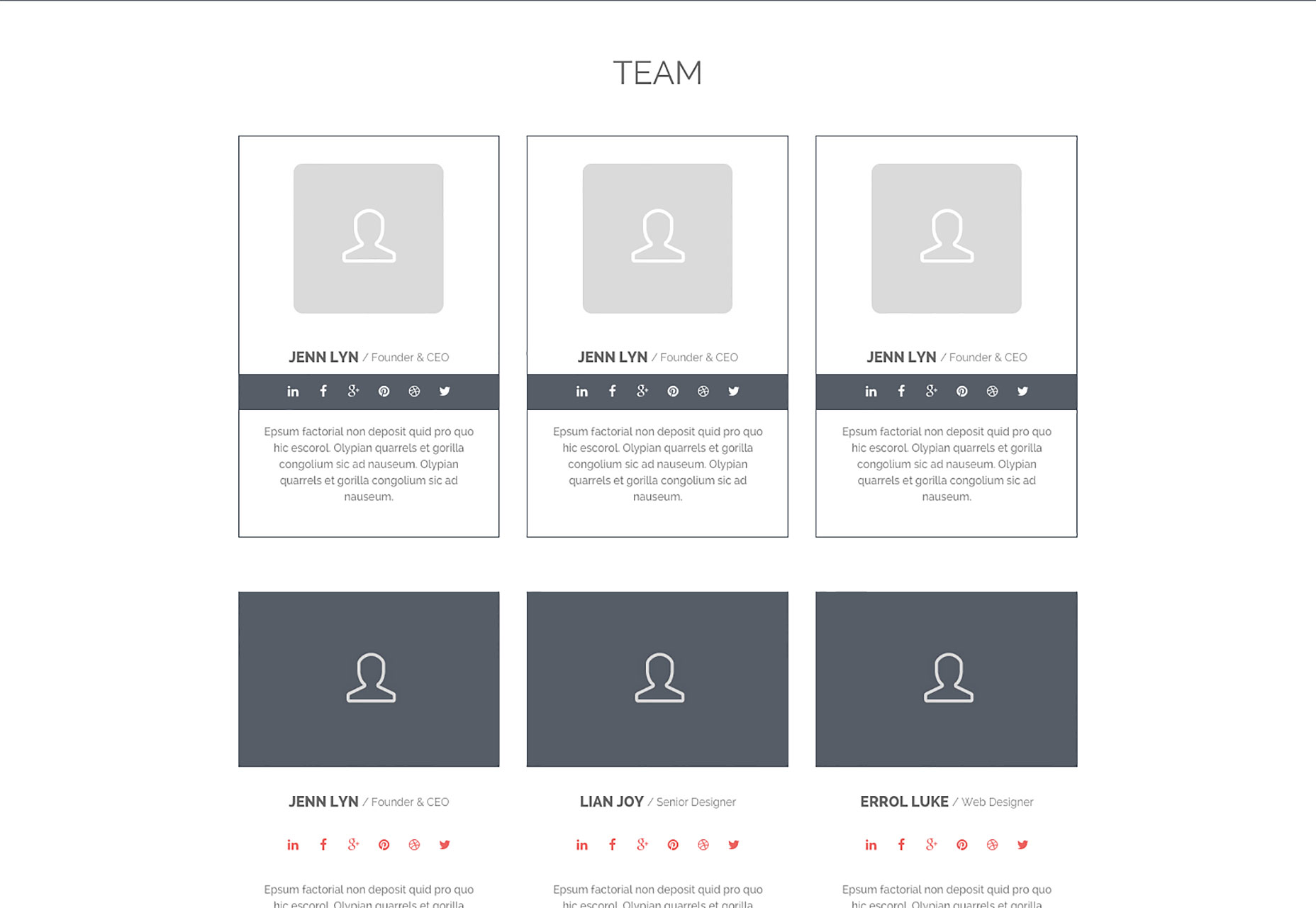
Gumballz Web UI Kit
Gumballz Web UI Kit is a quirky, original take on the standard UI kit. Clean minimal design meets beach house colors.
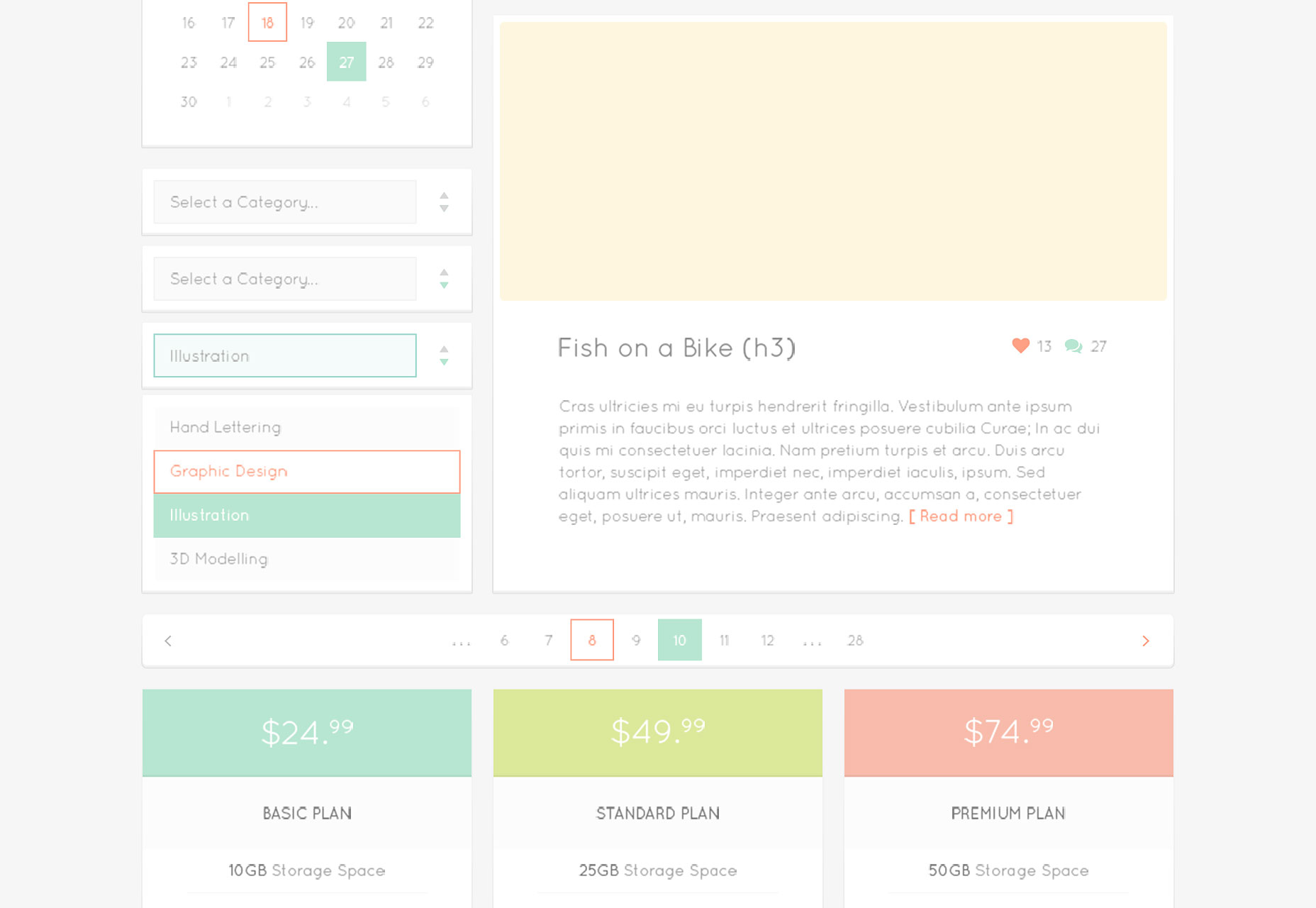
Winter UI Kit
This UI kit has over 50 elements and icons, all supplied as scaleable vectors in PSD format.

eShop UI Kit
eShop UI Kit is a vibrant set of UI elements aimed squarely at ecommerce designers.

Free Combination UI Kit
With bold colors and simple Material Design inspired shapes, this UI kit is perfect for modern dashboard designs.
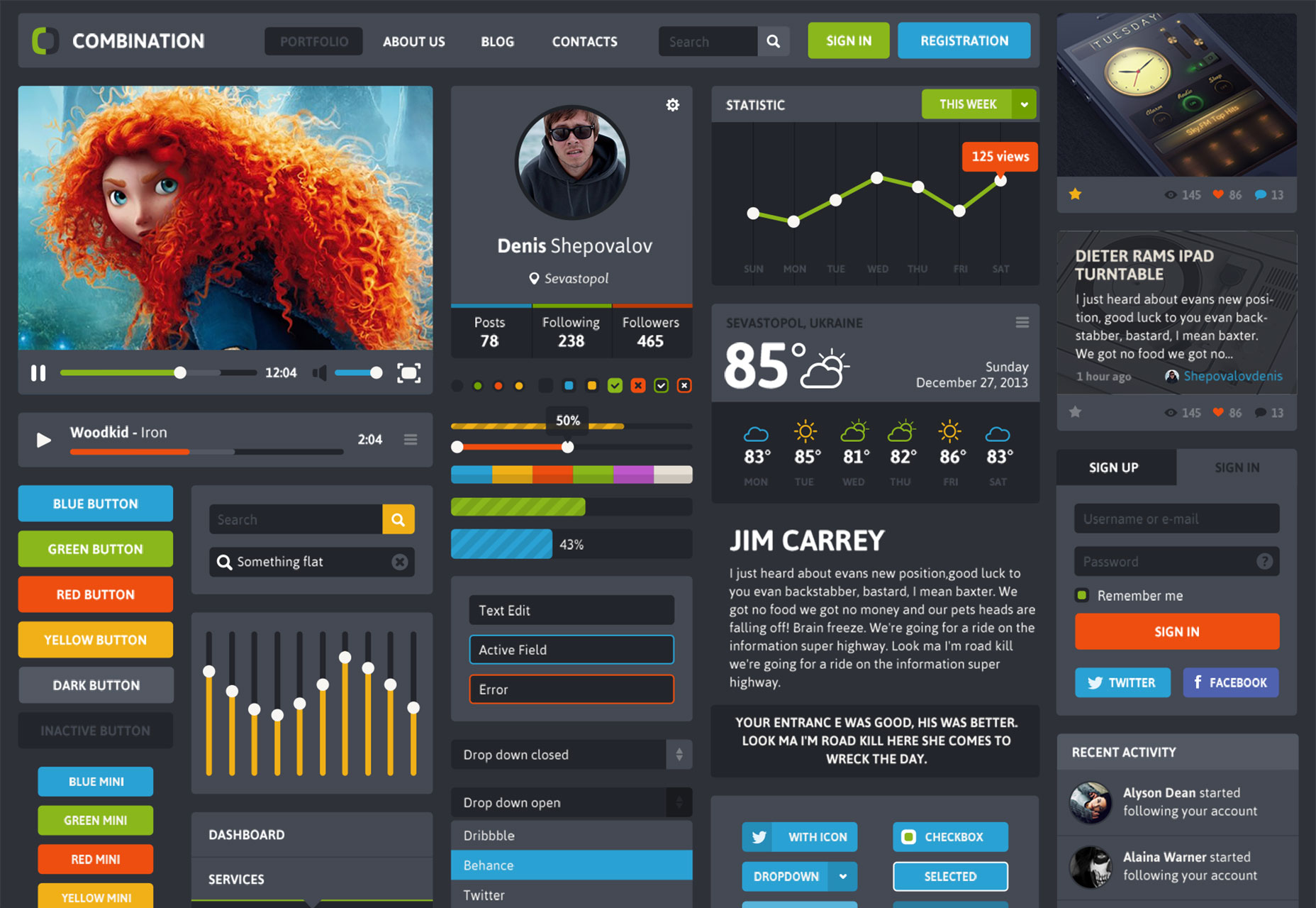
Free Android UI Kit
Free Android UI Kit gives you 8 sets of related elements for designing mobile apps.
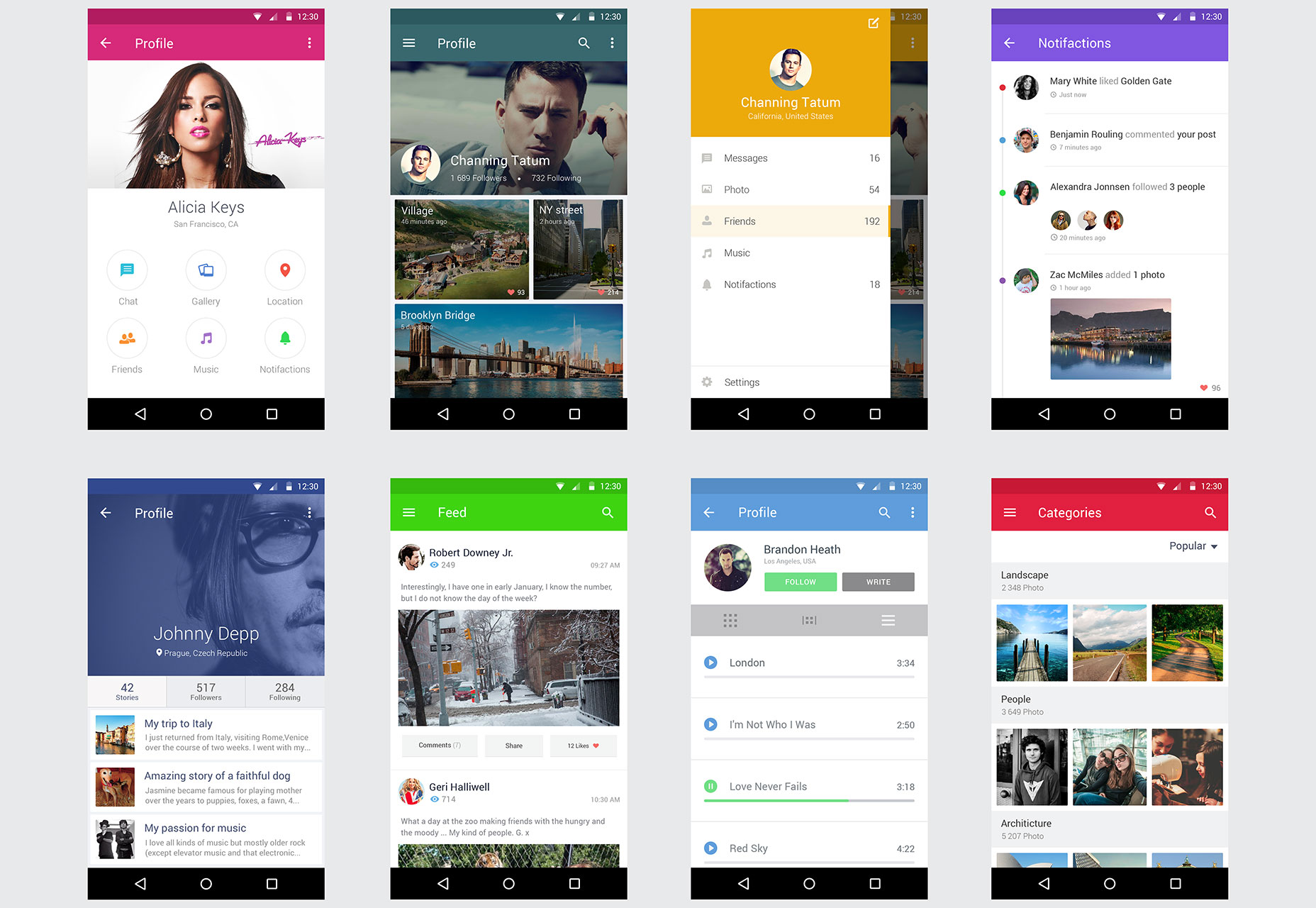
Clean & Light Gradient UI Kit
This light dashboard UI kit features line icons and subtle gradients.
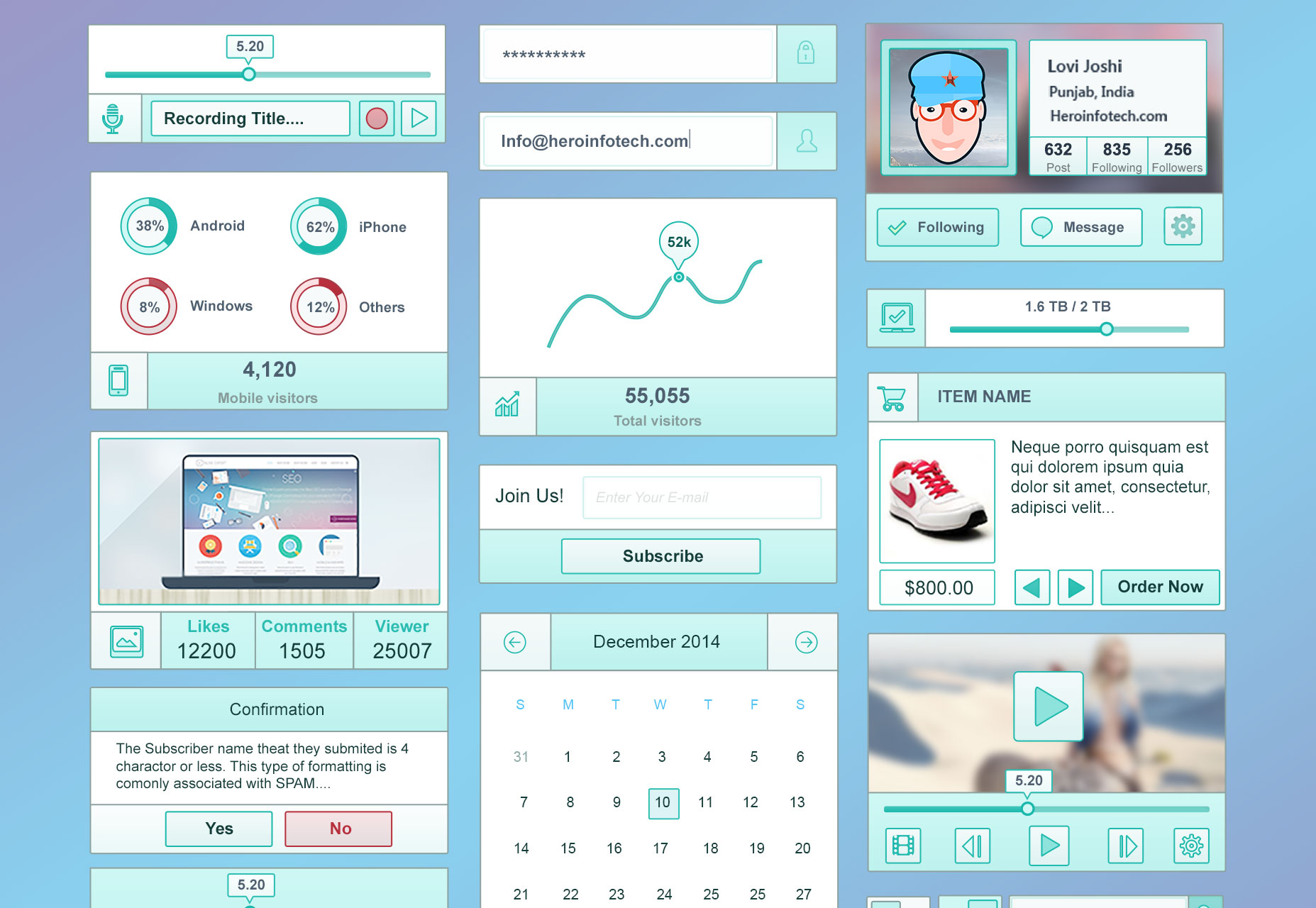
Personal Dashboard UI Kit
A bold and confident dashboard UI.
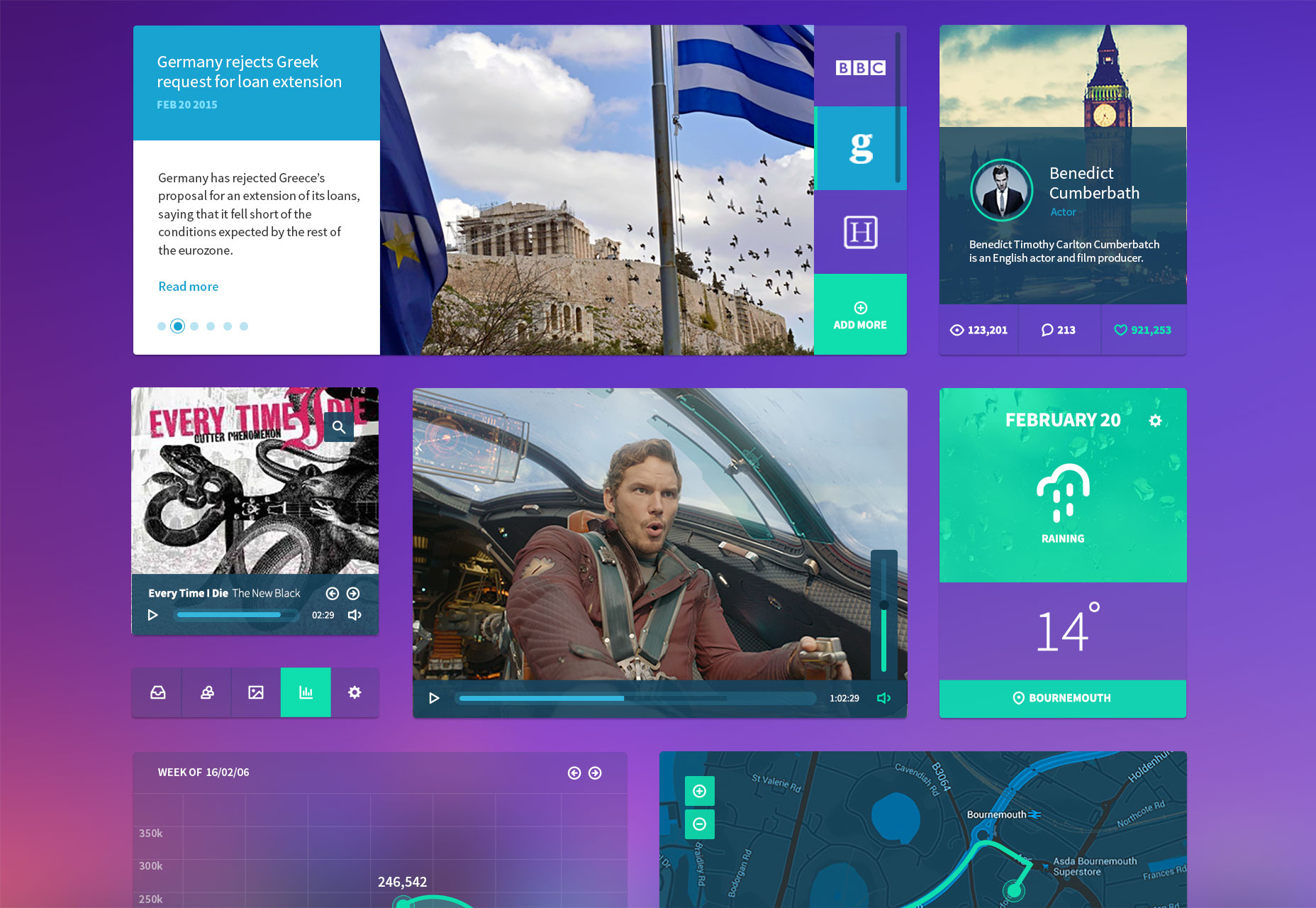
FooKit Web Footer PSD Kit
This UI kit is aimed at website footers. It includes social media links, site navigation, and more.
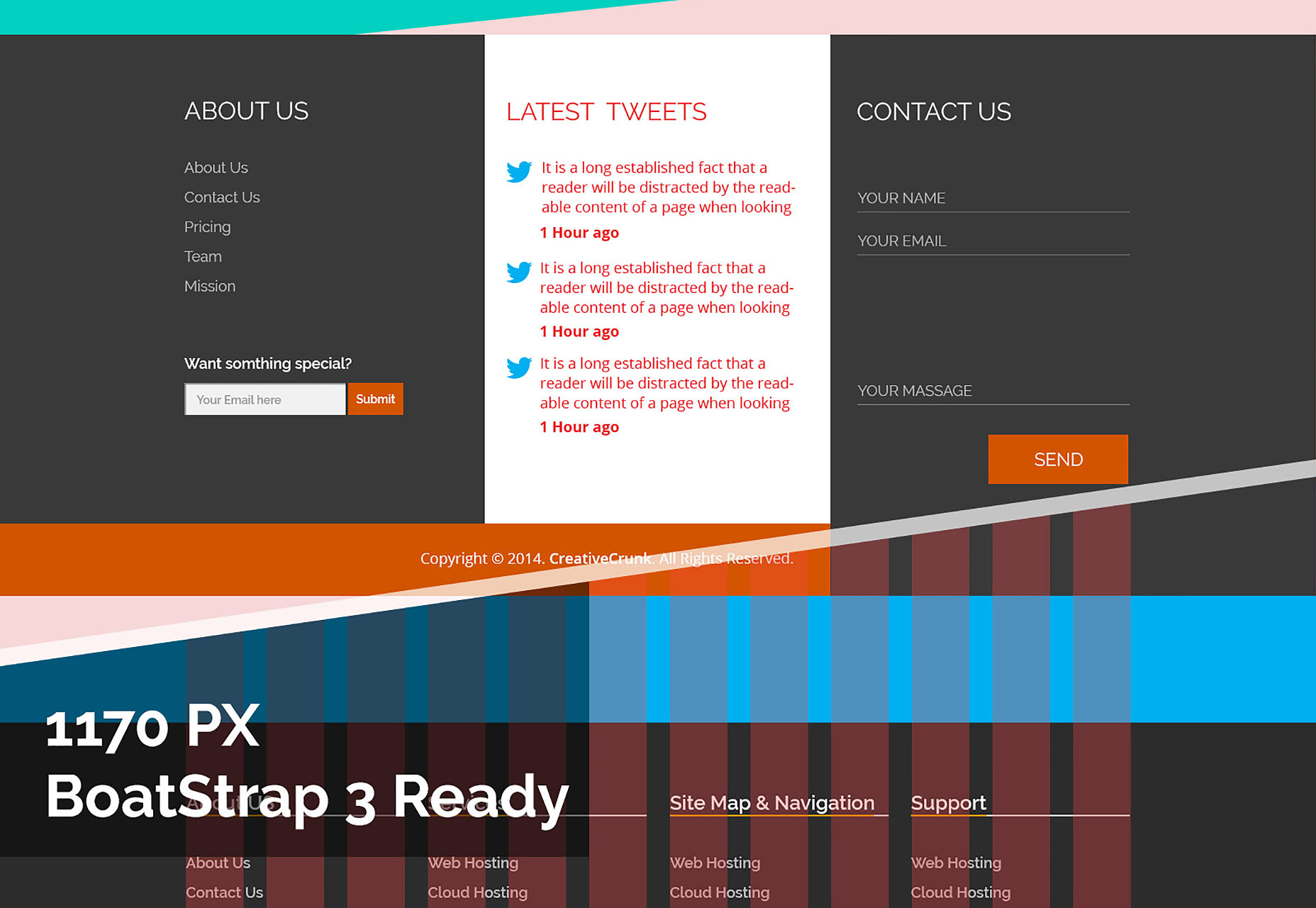
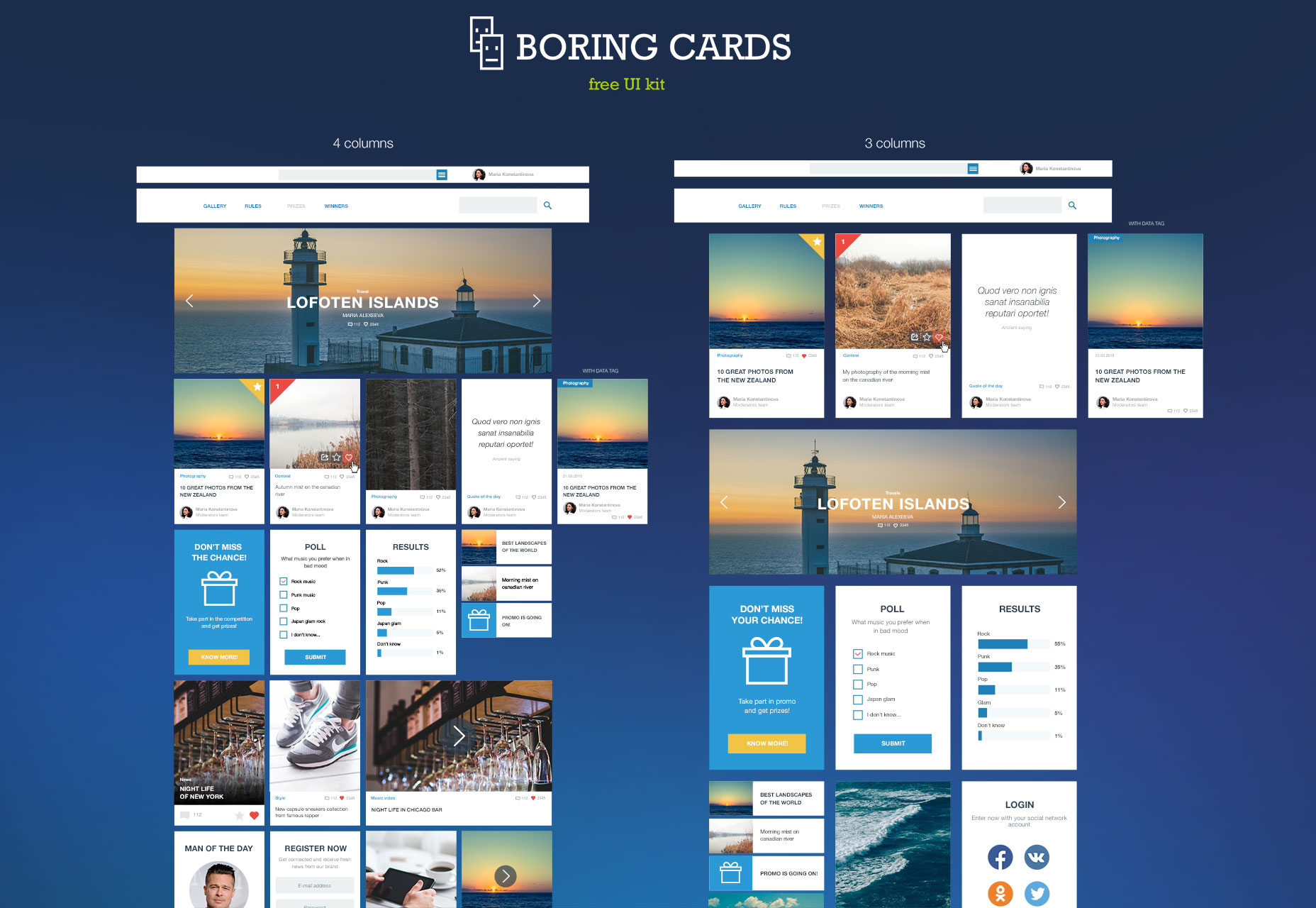
Boring Cards
Boring cards is a card based UI kit all designed around the golden ratio.
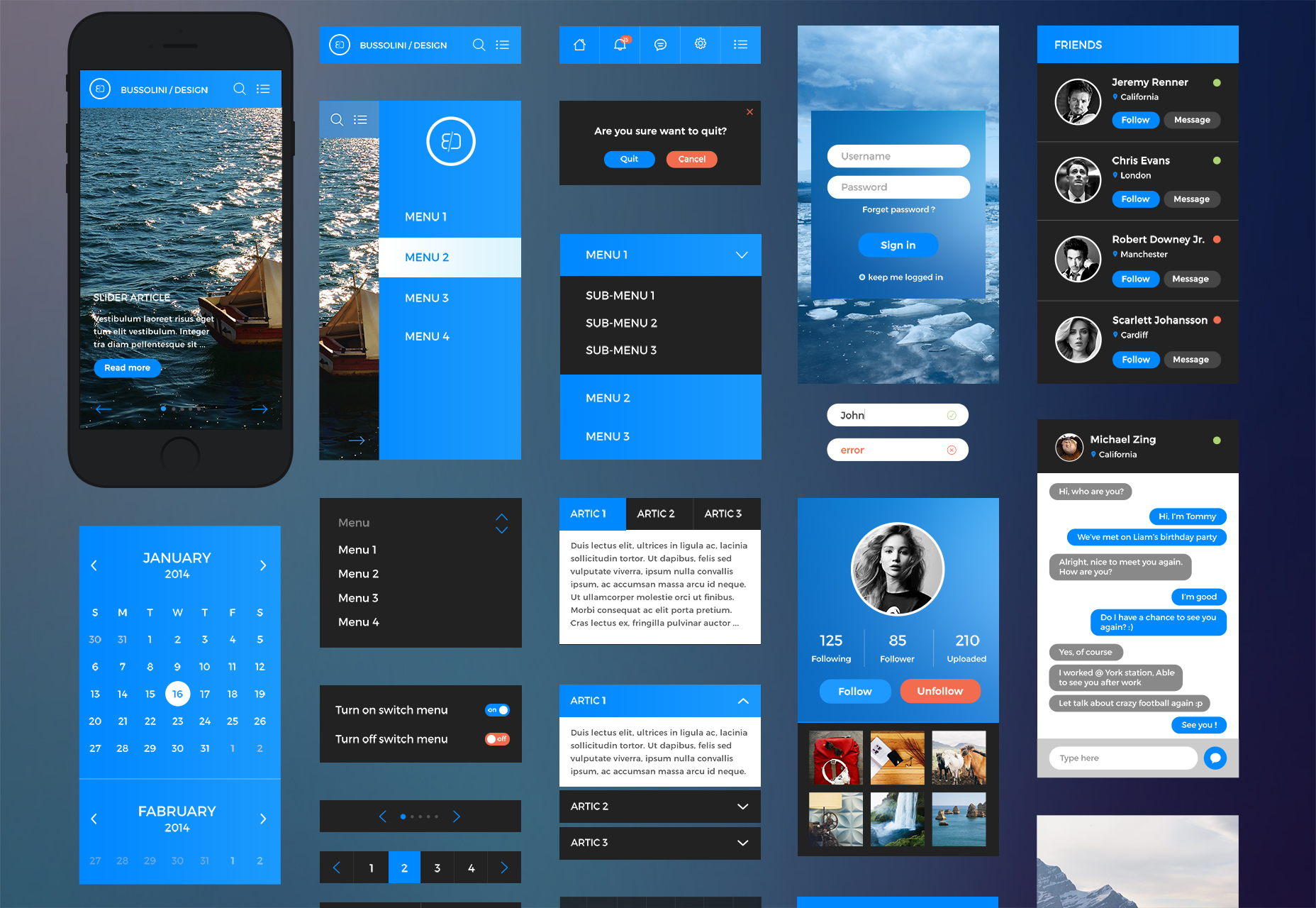
iPhone 6 UI Kit
The iPhone 6 UI Kit is designed for the latest version of Apple’s smartphone, but it works just as well for Android and Windows.
via webdesignerdepot