当初配置springmvc的时候,因为是第一次使用springmvc,为图快捷,因而大量从网上查找入门信息。
遗憾的是,网上的配置真是五花八门,让我彻底凌乱。
至今阅读文章不少于300余篇,回头适当整理下这个。
spring mvc的mvc:annotation-driven以及日期的处理摘自
http://blog.csdn.net/xiejx618/article/details/24745207 2014-04-29
<mvc:annotation-driven />是什么意思?
参考手册http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/3.2.4.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/pdf/spring-framework-reference.pdf会讲得比较清楚
17.15 Configuring Spring MVC讲到<mvc:annotation-driven />就是
A。注册了
一个RequestMappingHandlerMapping,
一个RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
和一个ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
(其中包括)支持使用注解标注在Controller方法的处理请求,例如@RequestMapping ,@ExceptionHandler等等
B。它还执行以下操作:1. Spring 3 style type conversion through a ConversionService instance in addition to the JavaBeans PropertyEditors used for Data Binding.2. Support for formatting Number fields using the @NumberFormat annotation through the ConversionService.3. Support for formatting Date, Calendar, Long, and Joda Time fields using the @DateTimeFormat annotation.4. Support for validating @Controller inputs with @Valid, if a JSR-303 Provider is present on the classpath.5. HttpMessageConverter support for @RequestBody method parameters and @ResponseBody method return values from @RequestMapping or @ExceptionHandler methods.
C。Details for B5This is the complete list of HttpMessageConverters set up by mvc:annotation-driven:• ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter converts byte arrays.• StringHttpMessageConverter converts strings.• ResourceHttpMessageConverter converts to/from org.springframework.core.io.Resource for all media types.• SourceHttpMessageConverter converts to/from a javax.xml.transform.Source.• FormHttpMessageConverter converts form data to/from a MultiValueMap<String,String>.• Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter converts Java objects to/from XML — added if JAXB2 is present on the classpath.• MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter (or MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter) converts to/from JSON — added if Jackson 2 (or Jackson) is present on the classpath.• AtomFeedHttpMessageConverter converts Atom feeds — added if Rome is present on the classpath.• RssChannelHttpMessageConverter converts RSS feeds — added if Rome is present on the classpath.其实相信在大多数实际应用环境中使用mvc:annotation-driven是少数,因为一般都满足不了需求,但想快速搭配环境还是比较适合的.当使用java config,记得有文章介绍不推荐配置RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
如果不使用mvc:annotation-driven,日期又如何处理.
spring mvc 1. 默认是支持yyyy-MM-dd格式的字符串转换为java的java.util.Date.包括spring mvc框架本身和spring mvc支持的jackson.
2. 对于其它格式的日期的字符串与Java的Date对象相互转化,一样可分为两种情况:
2.A:一种普通请求,前台的日期字符串与后台的Java Date对象转化,此情况,应使用spring mvc本身的内置日期处理.
2.B:另一种将参数写进请求体里面,使用application/json这样的mediaType发请求,对于此情况,应使用Jackson的序列化和反序列化来处理.
一.第1种情况(不要忘了加joda-time包哦):
1.先使用@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")在Controller的方法参数或VO的属性使用.
2.如果不使用mvc:annotation-driven,那么使用数据绑定来处理@DateTimeFormat这样的注解.配置例子如下:
- <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping" />
- <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
- <property name="webBindingInitializer">
- <bean class="org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer">
- <property name="conversionService" ref="conversionService" />
- </bean>
- </property>
- <property name="messageConverters">
- <list>
- <bean id="stringHttpMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"/>
- <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
- <property name="supportedMediaTypes">
- <list>
- <value>application/json; charset=UTF-8</value>
- <value>text/html; charset=UTF-8</value>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
- <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.DefaultFormattingConversionService"/>
二.第2种情况:1.继承定义序列化和反序列化类.例子:- public class DateJsonSerializer extends JsonSerializer<Date> {
- public static final SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
- @Override
- public void serialize(Date date, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator, SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException {
- jsonGenerator.writeString(format.format(date));
- }
- }
- public class DateJsonDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<Date> {
- public static final SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
- @Override
- public Date deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException {
- try {
- return format.parse(jsonParser.getText());
- } catch (ParseException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }
@JsonSerialize(using = DateJsonSerializer.class)
@JsonDeserialize(using = DateJsonDeserializer.class)
private Date createTime;
作者小注:
spring3.2开始不推荐使用setMediaTypes等直接设置这些数据, 而是通过ContentNegotiationManager(ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean) <bean class="ContentNegotiatingViewResolver">
<property name="contentNegotiationManager">
<bean class="ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="mediaTypes">
<props>注入即可
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
使用spring MVC构建RESTful Web Services(一):准备
摘自 2014-05-18 http://my.oschina.net/wuxianAbs/blog/266136
现在系统之间的交互越来越多,为实现跨语言访问,之前使用SOAP格式的webService,但接口开发比较复杂,且使用XML作中间语言,对XML的掌握也要求较高,最近这几年兴起了rest风格的webService调用,使用HTTP协议,接口不需要wsdl定义,数据传输格式既可以用JSON也可以用XML,简单了很多,它已经飞入寻常开发人员身边了,而且框架的选择也很多,甚至用原生的sevlet都能实现。
从spring MVC3开始,就支持REST风格的编程,配置更简单,可以全部用注解实现,这次就使用它来完成我们的功能。
一、使用框架
Spring MVC :3.2.8.RELEASE 。spring4新功能还没看,就用这个版本吧
数据库访问:待定,前期不准备用数据库,如果有精力再加吧
maven 这个不解释
二、spring MVC配置
spring MVC的配置比较简单,主要配置两处:web.xml和spring自己的配置
web.xml配置如下。有三处需要注意。
1.web.xml有两处指定了spring配置文件路径,但作用不同。
A. 在context-param中指定的路径创建的是通用的spring管理bean,用来管理我们的service层及其以下的资源、事务、aop等。
B. 在servlet中定义的DispatcherServlet是spring MVC的定义,它用来管理web层资源。因为是自家东西,集成也比较方便。web层的spring application会继承通用层的spring application,方便我们调用底层服务。
2.在定义DispatcherServlet的匹配模式的时候,不再使用常用的"*.action"或"*.do",而是使用"/",表示对所有资源的访问都会进入spring MVC,这样我们访问的时候不需要带后缀,直接以localhost:8080/restbucks/coffee这种url访问。而且后缀我们另做他用:客户端用后缀来标识想要的数据格式,我们会根据后缀返回对应格式的数据。比如请求的url带".xml"后缀表示你想要XML格式的数据,".json"后缀表示你想要JSON格式的数据,后面会讲到如何配置。
3.在正常的web项目中,我们都免不了会有jsp页面和静态资源,为了能正常访问,我们需要做一些设置。有好几种解决办法,这里使用最简单,效率也最高的一种。将不需要spring MVC处理的文件后缀在web.xml里显示标识出来,让web服务器的默认servlet处理,不走spring MVC。也可以使用spring MVC提供的功能。参看<mvc:resources/>和<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>的使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
classpath*:applicationContext.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>restBucks</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/restBucks-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>restBucks</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
spring文件配置。有两个配置文件,一个是spring的,一个是spring MVC的。下面是spring的配置文件,指定扫描的包,并且扫描除了标注Controller注解之外的所有类。Controller这个注解是spring MVC用来标注一个类是否是web控制器。
1 2 3 | <context:component-scan base-package="me.riverslob.restBucks">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
|
spring MVC的XML配置如下,使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>开启spring MVC的默认功能,随后会根据我们的需要来自定义。component-scan定义只扫描指定包的标注Controller注解的所有类。
1 2 3 4 | <mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="me.riverslob.restBucks" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
|
三、Controller
因为使用了注解,spring MVC控制器的定义也比较简单,下面是一个简单的例子。msgHandleService是底层提供的服务,可以看到spring MVC和spring整合的很好,我们用Autowired注解就框架就会自动帮我们注入进来。
spring MVC中,每个方法都是一个单独的控制器,处理一个web请求。所以我们常常把一个资源的CRUD请求放在一个类中。
在下面的例子中我们使用了这么几种注解:
| 注解名称 | 注解范围 | 说明 |
| Controller | 类 | 标识类会被spring MVC扫描管理 |
RequestMapping
| 类或方法 | 标识请求路径,放在类上,表示通用前缀,方法上的value值会与类上的value值拼接成全访问路径。参数:
value:请求路径
method:限制当前url的请求方式,有GET、POST、PUT等 |
| RequestParam | 方法入参 | 将request中的参数取出当作参数传入,可以处理简单类型,复杂类型可以自动转换 |
| PathVariable | 方法入参 | 可以看到RequestMapping的value值里可以有通配符,我们可以用PathVariable注解把通配符里的值取出当作参数传入.这种使用方法大家称为URL模板 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | @Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/webChatReceive")
public class WebChatReceiveController {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WebChatReceiveController.class);
@Autowired
private WebChatMsgHandleService msgHandleService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void checkSignature(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
String signature = request.getParameter("signature");
String timestamp = request.getParameter("timestamp");
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/qrrecords",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView showQrCodeRecords(@RequestParam("name") String param) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("/webchat/qrrecordlist.jsp");
List<QrCodeScanRecord> data = msgHandleService.showQrCodeScanRecords();
mv.addObject("data", data);
return mv;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/qrrecords/{id}")
public ModelAndView showQrCodeRecords(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("/webchat/qrrecordEdit.jsp");
QrCodeScanRecord data = msgHandleService.showQrCodeScanRecordsById(id);
mv.addObject("data", data);
return mv;
}
}
|
spring MVC控制器方法的参数个数没有要求,可以随意增减,框架会根据参数类型自动为我们填充相应数据。参数可以有:@RequestParam标识的参数(从request里取得)、@PathVariable标识的参数(从URL模板中取得)、HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、自己定义的POJO(框架会自动将request里的数据绑定成对象)、BindingResult(参数绑定失败的信息)
spring MVC控制器方法的返回类型也没有要求,有下面几种:ModelAndView(视图和数据信息)、View(视图信息)、String(试图的路径)、void(不返回路径)
除了上面说的,在做web服务时候,下面这种用法全比较多。可以看到,入参是我们自定义类型,且前面多了@RequestBody注解,方法直接返回我们生成的数据,且前面多了@ResponseBody注解。这两个注解会经常用到,它是框架自动帮我们做“java对象<--->JSON或XML格式数据”转换的标志。随后我们会说到:message converter
1 2 3 4 5 | @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody WsUser create(@RequestBody WsUser user) {
WsUser user=wsUserService.create(user);
return user;
}
|
使用spring MVC构建RESTful Web Services(二):消息转换
摘自2014-05-20 http://my.oschina.net/wuxianAbs/blog/266689
在前一节说到,如果在控制器中使用@ResponseBody或@RequestBody,spring MVC就会自动帮我们做“java对象<--->对应格式数据”的转换,用到的就是message converter。
消息转换的最上层是HttpMessageConverter,这是一个接口,它定义了消息转换实现类需要提供的方法:
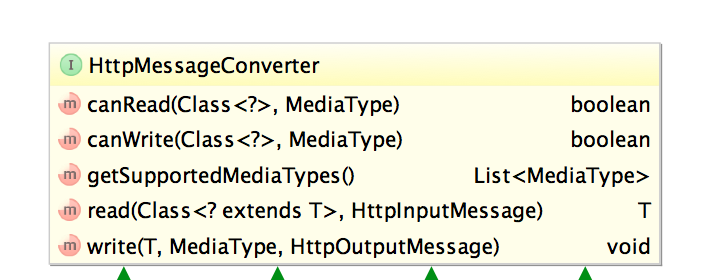
根据方法名我们可以猜测其功能:canRead确定是否可以将数据转换为java对象,read则负责将数据转换为java对象;反之,canWrite确定是否可以将java对象转换为指定格式数据,write负责把java对象转换为对应格式的数据。这里有一个很重要的概念,就是MediaType,可以看到,messageConverter在做canWrite和canRead判断时,就是根据java对象类型和MediaType.
MediaType:互联网媒体类型,一般就是我们所说的 MIME 类型,用来确定请求的内容类型或响应的内容类型。
注:Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 如果您的请求中含有 Accept:“*/*”,则可以匹配功能处理方法上的如“text/html”、“text/*”,“application/xml”等。
媒体类型格式:type/subtype(;parameter)?
type 主类型,任意的字符串,如 text,如果是*号代表所有;
subtype 子类型,任意的字符串,如 html,如果是*号代表所有;
parameter 可选,一些参数,如 Accept 请求头的 q 参数, Content-Type 的 charset 参数。
详见 http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-3.7
常见媒体类型:
text/html : HTML 格式
text/plain :纯文本格式
text/xml :XML 格式
image/gif :gif 图片格式 image/jpeg :jpg 图片格式 image/png:png 图片格式
application/x-www-form-urlencoded : <form encType=””>中默认的 encType,form 表单数据被编码为 key/value 格式发 送到服务器(表单默认的提交数据的格式)。
multipart/form-data : 当你需要在表单中进行文件上传时,就需要使用该格式;
application/xhtml+xml :XHTML 格式
application/atom+xml :Atom XML 聚合格式
application/pdf :pdf 格式
application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)。
application/xml: XML 数据格式
application/json : JSON 数据格式
可见,每个messageConverter会处理一个或几个MediaType到java对象的读、写转换。通过下面的类结构图我们就会一目了然。

下面说说我们经常用到的messageConverter:
1.StringHttpMessageConverter
它默认处理MediaType是text/plan和*/*(所有类型)的数据到java的转换。即String的转换处理,请注意,它默认的字符编码是ISO-8859-1,为避免乱码,我们改成UTF-8。spring bean的声明方式如下,也可以直接new 对象使用。因为它的构造函数中有默认编码参数,所以可以像下面这样设置。
1 2 3 | <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<constructor-arg name="defaultCharset" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
|
我们还可以调整它支持的MediaType,比如只支持text/plan:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/plan;charset=utf-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
|
2.FormHttpMessageConverter
我们程序里经常会有“http:sample.com/url?param1=value1¶m2=value2……”这种URL的情况,看到好多朋友if、else的拼,我都深表同情。如果用FormHttpMessageConverter该多方便啊,它只处理java类型是MultiValueMap的数据,这是spring自定义的类型,扩展自Map.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | MultiValueMap<String, Object> formData = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, Object>();
formData.add("media", resource);
formData.add("filename", filename);
formData.add("filelength", Long.toString(resource.contentLength()));
formData.add("filelength", Long.toString(17408));
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA);
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, Object>>(formData, headers);
AccessTokenModel tokenModel = getRestTemplate().postForObject(MULTIPART_UPLOAD_URL,requestEntity, AccessTokenModel.class);
|
上面这个例子用到了spring提供的RestTemplate来请求URL,我们请求是POST形式,RestTemplate的方法名开头表示了URL请求类型,postForObject表示我们请求方式是POST,且我们要求返回java对象数据,这里返回的是AccessTokenModel对象,可以看到,它里面封装了很多细节,我们只需要准备数据,然后通过它调用即可,数据转换全部交由它来完成。
在调用postForObject方法时,我们传了一个参数类型是HttpEntity的对象,它用来指示RestTemplate我们的数据和数据格式,这里是MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA,即multipart/form-data,如果不需要上传文件,可以指定MediaType是application/x-www-form-urlencoded,即form表单数据。这两种MediaType都由FormHttpMessageConverter来处理。
spring bean的声明方式如下,
1 | <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.FormHttpMessageConverter"/>
|
3.Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter
这个是用来处理JAXB的XML与java对象间的数据转换的。之前我介绍过JAXB,它是SOAP版的一部分,虽然SOAP已经不受宠,但JAXB真心好用。想想,只需要在类上加些注解,就可以自定义生成的格式信息,这是何等的方便,所以,转xml的工作就交给它了。而且它还有一个优势,随后会说到。
4.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
这个是java转JSON的消息转换类。可能有人会问,java转JSON的工具千千万,为什么要选它呢?
原因一、好用,支持java、JSON转换;支持直接操纵JSON流对象;支持一些低级操作,如果效率优先,可以使用它们。单从这三点,不比其他工具差
原因二、spring MVC已经内置支持,只需简单设置,不需要自己再去写一套来适配了
原因三、上面说了,JAXB有一个优势,使用广泛。它的一些注解已经成为标准。而jackson适配了JAXB的注解,提供了JaxbAnnotationIntrospector这个模块,一个注解,两处使用,何其方便。再者现在主流格式就是XML和JSON,有这两个就够了。
下面看用JAXB注解定义的java对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | @XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "", propOrder = {
"name",
"pwd","age","birthday","inner"
})
@XmlRootElement(name = "ConverterVO")
public class ConverterVO {
private String name;
private String pwd;
private Integer age;
@XmlElement(name = "birthday")
@XmlJavaTypeAdapter(DateAdapter.class)
private Date birthday;
private InnerConverterVO inner;
}
public class InnerConverterVO{
private String name;
private Integer innerId;
}
|
生成的xml数据如下:
1 2 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<ConverterVO><name>xiaowang</name><pwd>123456</pwd><age>15</age><birthday>1996-10-15 00:50:17</birthday><inner><innerId>1111</innerId><name>innerConvertVO</name></inner></ConverterVO>
|
生成的JSON数据如下:
1 | {"name":"xiaowang","pwd":"123456","age":15,"birthday":"1996-10-15 00:46:34","inner":{"name":"innerConvertVO","innerId":1111}}
|
现在,我们的spring MVC的配置文件就变成了这样:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | <mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="false">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.FormHttpMessageConverter"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.xml.Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="objectMapper" ref="objectMapper"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<constructor-arg name="defaultCharset" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<context:component-scan base-package="me.rivearslob.restBucks" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<bean id="objectMapper" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperFactoryBean">
<property name="annotationIntrospector">
<bean class="com.fasterxml.jackson.module.jaxb.JaxbAnnotationIntrospector"/>
</property>
</bean>
|
ps:关于MediaType一块使用了开涛整理的信息。