JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。
JDBC访问数据库的步骤:
1.加载数据库驱动
2.获得数据库连接
3.创建SQL语句
4.执行查询
5.遍历结果集
6.关闭数据库连接
下面看一个小程序:
 package com.jspring.jdbc;
package com.jspring.jdbc;

 import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Connection;
 import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
 import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
 import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLException;
 import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Statement;


 public class Demo1
public class Demo1  {
{
 public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String args[])


 {
{
 query();
query();
 }
}
 public static void query()
public static void query()


 {
{
 Connection conn=null;
Connection conn=null;
 //1.加载数据库驱动
//1.加载数据库驱动

 try
try  {
{
 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
 //DriverManager 驱动程序管理器 在数据库和相应驱动程序之间建立连接
//DriverManager 驱动程序管理器 在数据库和相应驱动程序之间建立连接
 //2.获得数据库连接
//2.获得数据库连接
 conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/jdbc_db","root","1234");
conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/jdbc_db","root","1234");
 //3.创建语句
//3.创建语句
 String sql="select * from UserTbl";
String sql="select * from UserTbl";
 //返回一个执行SQL的语句
//返回一个执行SQL的语句
 Statement stmt = null;
Statement stmt = null;
 stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt = conn.createStatement();
 //返回查询的
//返回查询的
 //4.执行语句
//4.执行语句
 ResultSet rs = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
 rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
 //5.遍历结果集
//5.遍历结果集
 while(rs.next())
while(rs.next())


 {
{
 int id=rs.getInt(1);
int id=rs.getInt(1);
 String username=rs.getString(2);
String username=rs.getString(2);
 String password=rs.getString(3);
String password=rs.getString(3);
 int age=rs.getInt(4);
int age=rs.getInt(4);
 System.out.println(id+":"+username+":"+password+":"+age);
System.out.println(id+":"+username+":"+password+":"+age);
 }
}

 } catch (Exception e)
} catch (Exception e)  {
{
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();

 }finally
}finally {
{

 if(conn!=null)
if(conn!=null) {
{

 try
try {//5.关闭数据库连接
{//5.关闭数据库连接
 conn.close();
conn.close();

 }catch(SQLException e)
}catch(SQLException e) {
{
 conn=null;
conn=null;
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}


1.此程序首先要在这个程序所在的工程中插入连接数据库的jar包(然后右击选择build path-----add to build path),然后才能执行程序否则会出现以下错误提示:
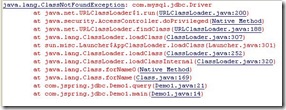
这个程序通过执行
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
这个语句实现加载驱动,因为我用的是MYSQL的数据库,所以加载的mysql的驱动,如果你用的是其他数据库,那就要加载其他数据库的jar包。
2.和数据库建立连接通过
conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/jdbc_db","root","1234");
语句,getConnection函数中三个参数分别是url,user,password
3.创建语句,在这个程序中只建立了一个查询语句,我们可以根据自己的业务需求建立其他的语句,例如插入,更新等语句
4.Statement是静态的SQL语句,用来盛放SQL语句,他有一个子类为PreparedStatement为预编译静态语句
5.ResultSet 是用来盛放查询结果的一个集合
程序运行结果:
如果usertbl表中有数据就会打印在控制台上如
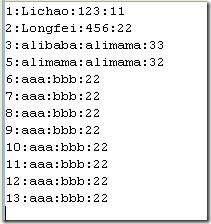
如果usertbl表中没有数据那么控制台上就没有任何数据
如果数据库中没有这个表则会出现
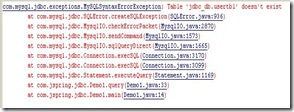
在使用JDBC时一定要加载数据库驱动!
一般情况下,我们会采用下面这种方法和数据库进行连接
将数据库的驱动连接和url,user,password都写到配置文件中,通过从配置文件中读数据来建立连接,看下面程序

 public class ConnectionUtil
public class ConnectionUtil  {
{

 public Connection openConnection()
public Connection openConnection() {
{
 String driver = "";
String driver = "";
 String url = "";
String url = "";
 String user = "";
String user = "";
 String password = "";
String password = "";
 Properties prop = new Properties();
Properties prop = new Properties();
 Connection conn = null;
Connection conn = null;

 try
try  {
{
 //加载属性文件
//加载属性文件
 prop.load(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("DBConfig.properties"));
prop.load(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("DBConfig.properties"));
 driver = prop.getProperty("driver");
driver = prop.getProperty("driver");
 url = prop.getProperty("url");
url = prop.getProperty("url");
 user = prop.getProperty("user");
user = prop.getProperty("user");
 password = prop.getProperty("password");
password = prop.getProperty("password");
 //Class.forName加载驱动
//Class.forName加载驱动
 Class.forName(driver);
Class.forName(driver);
 //DriverManager获得连接
//DriverManager获得连接
 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
 return conn;
return conn;

 } catch (Exception e)
} catch (Exception e)  {
{
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 return null;
return null;
 }
}
 }
}


在和数据库进行连接时,我们只需要调用这个类就可以了
在第一个程序中我们提到了一个PreparedStatement类,现在我们看一下关于这个类的使用情况

 public class Main
public class Main  {
{


 public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String[] args)  {
{
 Customer c = new Customer();
Customer c = new Customer();
 c.setName("hans");
c.setName("hans");
 c.setEmail("583480612@qq.com");
c.setEmail("583480612@qq.com");
 TestPrepareStatement.add(c);
TestPrepareStatement.add(c);
 }
}

 public static void add(Customer c)
public static void add(Customer c)  {
{
 Connection conn = new ConnectionUtil().openConnection();
Connection conn = new ConnectionUtil().openConnection();
 String sql = "insert into CustomerTbl(name,email) values(?,?)";
String sql = "insert into CustomerTbl(name,email) values(?,?)";

 try
try  {
{
 PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
 pstmt.setString(1, c.getName());
pstmt.setString(1, c.getName());
 pstmt.setString(2, c.getEmail());
pstmt.setString(2, c.getEmail());
 pstmt.executeUpdate();
pstmt.executeUpdate();

 } catch (SQLException e)
} catch (SQLException e)  {
{
 e.printStackTrace();
e.printStackTrace();
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}


PreparedStatement为预编译静态SQL语句,就是在sql语句中留下一个缺口,由调用这个函数的的成员来补全。