本期开始讲Model层的开发,整合iBatis框架,iBatis是Apache旗下Java数据持久层的框架,跟Hibernate是同一类型的框架。大家可到它的官方网站去下载http://ibatis.apache.org/java.cgi,如下图:
我这里下载的是当前最新版本iBatis 2.3.4 , 下载之后,解压包是这样的:
我们在lib目录下,找到“ibatis-2.3.4.726.jar”文件,加入到我们项目的lib目录下,就行。在这里,我们先说下怎么学习这个iBatis框架:上图中,有个simple_example的文件夹,它里面就包含了一个超级简单且容易理解的例子,大家可以去学习一下。By the way,如果你学过Hibernate的话,你会发觉iBatis要比Hibernate好学很多。关于Hibernate和iBatis的争论,网上有很多,大家有兴趣可以去了解一下。
好,我们先建立数据库和设计数据库吧。我这项目用的是MySQL 5.0。生成数据库和数据表的SQL语句如下:
|
create database simpledb;
create table article
(
ID int auto_increment not null primary key,
TITLE varchar(25),
AUTHOR varchar(25),
CONTENT text,
PUBTIME date
);
|
这是我们常见的新闻表及其中的字段。
接下来,写一个与表对应的新闻类,Article.java,这个其实是POJO类,代码如下:
 package cn.simple.pojo;
package cn.simple.pojo;

 import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Date;


 public class Article
public class Article  {
{

 private int id;
private int id;
 private String title;
private String title;
 private String author;
private String author;
 private String content;
private String content;
 private Date pubtime;
private Date pubtime;


 /** *//***********getter和setter方法***********/
/** *//***********getter和setter方法***********/

 public int getId()
public int getId()  {
{
 return id;
return id;
 }
}

 public void setId(int id)
public void setId(int id)  {
{
 this.id = id;
this.id = id;
 }
}

 public String getTitle()
public String getTitle()  {
{
 return title;
return title;
 }
}

 public void setTitle(String title)
public void setTitle(String title)  {
{
 this.title = title;
this.title = title;
 }
}

 public String getAuthor()
public String getAuthor()  {
{
 return author;
return author;
 }
}

 public void setAuthor(String author)
public void setAuthor(String author)  {
{
 this.author = author;
this.author = author;
 }
}

 public String getContent()
public String getContent()  {
{
 return content;
return content;
 }
}

 public void setContent(String content)
public void setContent(String content)  {
{
 this.content = content;
this.content = content;
 }
}

 public Date getPubtime()
public Date getPubtime()  {
{
 return pubtime;
return pubtime;
 }
}

 public void setPubtime(Date pubtime)
public void setPubtime(Date pubtime)  {
{
 this.pubtime = pubtime;
this.pubtime = pubtime;
 }
}

 }
}

有了数据表和实体类,现在来写两者之间映射的配置文件Article.xml。代码如下:
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>

 <!DOCTYPE sqlMap
<!DOCTYPE sqlMap
 PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map 2.0//EN"
PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map 2.0//EN"
 "http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-2.dtd">
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-2.dtd">

 <sqlMap namespace="Article">
<sqlMap namespace="Article">

 <!-- Use type aliases to avoid typing the full classname every time. -->
<!-- Use type aliases to avoid typing the full classname every time. -->
 <typeAlias alias="Article" type="cn.simple.pojo.Article" />
<typeAlias alias="Article" type="cn.simple.pojo.Article" />

 <!--
<!--
 Result maps describe the mapping between the columns returned from a
Result maps describe the mapping between the columns returned from a
 query, and the class properties. A result map isn't necessary if the
query, and the class properties. A result map isn't necessary if the
 columns (or aliases) match to the properties exactly.
columns (or aliases) match to the properties exactly.
 -->
-->
 <resultMap id="ArticleResult" class="Article">
<resultMap id="ArticleResult" class="Article">
 <result property="id" column="ID" />
<result property="id" column="ID" />
 <result property="title" column="TITLE"/>
<result property="title" column="TITLE"/>
 <result property="author" column="AUTHOR"/>
<result property="author" column="AUTHOR"/>
 <result property="content" column="CONTENT"/>
<result property="content" column="CONTENT"/>
 <result property="pubtime" column="PUBTIME"/>
<result property="pubtime" column="PUBTIME"/>
 </resultMap>
</resultMap>

 <!--
<!--
 Select with no parameters using the result map for Account class.
Select with no parameters using the result map for Account class.
 -->
-->
 <select id="selectAllArticles" resultMap="ArticleResult">
<select id="selectAllArticles" resultMap="ArticleResult">
 select * from article
select * from article
 </select>
</select>

 <!--
<!--
 A simpler select example without the result map. Note the aliases to
A simpler select example without the result map. Note the aliases to
 match the properties of the target result class.
match the properties of the target result class.
 -->
-->
 <select id="selectArticleById" parameterClass="int" resultClass="Article">
<select id="selectArticleById" parameterClass="int" resultClass="Article">
 select
select
 ID as id,
ID as id,
 TITLE as title,
TITLE as title,
 AUTHOR as author,
AUTHOR as author,
 CONTENT as content,
CONTENT as content,
 PUBTIME as pubtime
PUBTIME as pubtime
 from Article
from Article
 where ID=#id#
where ID=#id#
 </select>
</select>

 <!-- Insert example, using the Account parameter class -->
<!-- Insert example, using the Account parameter class -->
 <insert id="insertArticle" parameterClass="Article">
<insert id="insertArticle" parameterClass="Article">
 insert into article (
insert into article (
 TITLE,
TITLE,
 AUTHOR,
AUTHOR,
 CONTENT,
CONTENT,
 PUBTIME
PUBTIME
 ) values (
) values (
 #title#,
#title#,
 #author#,
#author#,
 #content#,
#content#,
 #pubtime#
#pubtime#
 )
)
 </insert>
</insert>

 <!-- Update example, using the Account parameter class -->
<!-- Update example, using the Account parameter class -->
 <update id="updateArticle" parameterClass="Article">
<update id="updateArticle" parameterClass="Article">
 update article set
update article set
 TITLE = #title#,
TITLE = #title#,
 AUTHOR = #author#,
AUTHOR = #author#,
 CONTENT = #content#,
CONTENT = #content#,
 PUBTIME = #pubtime#
PUBTIME = #pubtime#
 where
where
 ID = #id#
ID = #id#
 </update>
</update>

 <!-- Delete example, using an integer as the parameter class -->
<!-- Delete example, using an integer as the parameter class -->
 <delete id="deleteArticleById" parameterClass="int">
<delete id="deleteArticleById" parameterClass="int">
 delete from article where ID = #id#
delete from article where ID = #id#
 </delete>
</delete>

 </sqlMap>
</sqlMap>

大家不要觉得这个映射文件很复杂,其实,这挺容易理解的,如果大家赖得写的话,可复制iBatis自带的simple_example下的例子的映射文件,然后修改一下就行。
有了表、实体类、表与实体之间的映射文件,之后,该做什么呢?学过Hibernate的朋友会想到那个数据库连接信息的配置文件,当然,iBatis也需要类似的文件,即SqlMapConfig.xml,代码如下:
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>

 <!DOCTYPE sqlMapConfig
<!DOCTYPE sqlMapConfig
 PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map Config 2.0//EN"
PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map Config 2.0//EN"
 "http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-config-2.dtd">
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-config-2.dtd">

 <sqlMapConfig>
<sqlMapConfig>

 <!-- Configure a built-in transaction manager. If you're using an
<!-- Configure a built-in transaction manager. If you're using an
 app server, you probably want to use its transaction manager
app server, you probably want to use its transaction manager
 and a managed datasource -->
and a managed datasource -->
 <transactionManager type="JDBC" commitRequired="false">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" commitRequired="false">
 <dataSource type="SIMPLE">
<dataSource type="SIMPLE">
 <property name="JDBC.Driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="JDBC.Driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
 <property name="JDBC.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/simpledb"/>
<property name="JDBC.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/simpledb"/>
 <property name="JDBC.Username" value="root"/>
<property name="JDBC.Username" value="root"/>
 <property name="JDBC.Password" value="root"/>
<property name="JDBC.Password" value="root"/>
 </dataSource>
</dataSource>
 </transactionManager>
</transactionManager>

 <!-- List the SQL Map XML files. They can be loaded from the
<!-- List the SQL Map XML files. They can be loaded from the
 classpath, as they are here (com.domain.data
classpath, as they are here (com.domain.data ) -->
) -->
 <sqlMap resource="cn/simple/pojo/Article.xml"/>
<sqlMap resource="cn/simple/pojo/Article.xml"/>
 <!-- List more here
<!-- List more here
 <sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Order.xml"/>
<sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Order.xml"/>
 <sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Documents.xml"/>
<sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Documents.xml"/>
 -->
-->

 </sqlMapConfig>
</sqlMapConfig>
一看这代码,也有点复杂,我的说法同上,大不了COPY,再略作修改,呵呵
好了,来写我们的业务逻辑层:
 package cn.simple.manager;
package cn.simple.manager;

 import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.IOException;
 import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Reader;
 import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLException;
 import java.util.List;
import java.util.List;
 import cn.simple.pojo.Article;
import cn.simple.pojo.Article;
 import com.ibatis.common.resources.Resources;
import com.ibatis.common.resources.Resources;
 import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClient;
import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClient;
 import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClientBuilder;
import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClientBuilder;


 public class ArticleManager
public class ArticleManager  {
{


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * SqlMapClient instances are thread safe, so you only need one. In this
* SqlMapClient instances are thread safe, so you only need one. In this
 * case, we'll use a static singleton. So sue me. ;-)
* case, we'll use a static singleton. So sue me. ;-)
 */
*/
 private static SqlMapClient sqlMapper;
private static SqlMapClient sqlMapper;


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * It's not a good idea to put code that can fail in a class initializer,
* It's not a good idea to put code that can fail in a class initializer,
 * but for sake of argument, here's how you configure an SQL Map.
* but for sake of argument, here's how you configure an SQL Map.
 */
*/

 static
static  {
{

 try
try  {
{
 Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("SqlMapConfig.xml");
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("SqlMapConfig.xml");
 sqlMapper = SqlMapClientBuilder.buildSqlMapClient(reader);
sqlMapper = SqlMapClientBuilder.buildSqlMapClient(reader);
 reader.close();
reader.close();

 } catch (IOException e)
} catch (IOException e)  {
{
 // Fail fast.
// Fail fast.
 throw new RuntimeException(
throw new RuntimeException(
 "Something bad happened while building the SqlMapClient instance."
"Something bad happened while building the SqlMapClient instance."
 + e, e);
+ e, e);
 }
}
 }
}


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * 查询列表
* 查询列表
 * @return
* @return
 * @throws SQLException
* @throws SQLException
 */
*/

 public static List<Article> selectAllArticles() throws SQLException
public static List<Article> selectAllArticles() throws SQLException  {
{
 return sqlMapper.queryForList("selectAllArticles");
return sqlMapper.queryForList("selectAllArticles");
 }
}


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * 插入数据
* 插入数据
 * @param article
* @param article
 * @throws SQLException
* @throws SQLException
 */
*/

 public static void insertArticle(Article article) throws SQLException
public static void insertArticle(Article article) throws SQLException  {
{
 sqlMapper.insert("insertArticle", article);
sqlMapper.insert("insertArticle", article);
 }
}


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * 更新数据
* 更新数据
 * @param article
* @param article
 * @throws SQLException
* @throws SQLException
 */
*/

 public static void updateArticle(Article article) throws SQLException
public static void updateArticle(Article article) throws SQLException  {
{
 sqlMapper.update("updateArticle", article);
sqlMapper.update("updateArticle", article);
 }
}


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * 删除数据
* 删除数据
 * @param id
* @param id
 * @throws SQLException
* @throws SQLException
 */
*/

 public static void deleteArticle(int id) throws SQLException
public static void deleteArticle(int id) throws SQLException  {
{
 sqlMapper.delete("deleteArticleById", id);
sqlMapper.delete("deleteArticleById", id);
 }
}


 /** *//**
/** *//**
 * 单查数据
* 单查数据
 * @param id
* @param id
 * @return
* @return
 * @throws SQLException
* @throws SQLException
 */
*/

 public static Article queryArticleById(int id) throws SQLException
public static Article queryArticleById(int id) throws SQLException  {
{
 Article article = (Article)sqlMapper.queryForObject("selectArticleById", id);
Article article = (Article)sqlMapper.queryForObject("selectArticleById", id);
 return article;
return article;
 }
}

 }
}

写一个Junit测试类来测试一下吧,代码如下:
 package cn.simple.manager;
package cn.simple.manager;

 import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLException;
 import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Date;
 import java.util.List;
import java.util.List;
 import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.Test;
 import cn.simple.pojo.Article;
import cn.simple.pojo.Article;


 public class ArticleManagerTest
public class ArticleManagerTest  {
{

 @Test
@Test

 public void testSelectAllArticles() throws SQLException
public void testSelectAllArticles() throws SQLException  {
{
 List<Article> list = ArticleManager.selectAllArticles();
List<Article> list = ArticleManager.selectAllArticles();

 for(Article a : list)
for(Article a : list) {
{
 System.out.println(a.getTitle() + a.getAuthor() + a.getContent() + a.getPubtime());
System.out.println(a.getTitle() + a.getAuthor() + a.getContent() + a.getPubtime());
 }
}
 }
}

 @Test
@Test

 public void testInsertArticle() throws SQLException
public void testInsertArticle() throws SQLException  {
{

 for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
{
 Article article = new Article();
Article article = new Article();
 article.setTitle("title-" + i);
article.setTitle("title-" + i);
 article.setAuthor("author-" + i);
article.setAuthor("author-" + i);
 article.setContent("content-" + i);
article.setContent("content-" + i);
 article.setPubtime(new Date());
article.setPubtime(new Date());
 ArticleManager.insertArticle(article);
ArticleManager.insertArticle(article);
 }
}
 }
}

 @Test
@Test

 public void testUpdateArticle() throws SQLException
public void testUpdateArticle() throws SQLException  {
{
 Article article = new Article();
Article article = new Article();
 article.setId(3);
article.setId(3);
 article.setTitle("title-title");
article.setTitle("title-title");
 article.setAuthor("author-author");
article.setAuthor("author-author");
 ArticleManager.updateArticle(article);
ArticleManager.updateArticle(article);
 }
}

 @Test
@Test

 public void testDeleteArticle() throws SQLException
public void testDeleteArticle() throws SQLException  {
{
 ArticleManager.deleteArticle(5);
ArticleManager.deleteArticle(5);
 }
}

 }
}

到此,我们的项目文件列表截图如下:
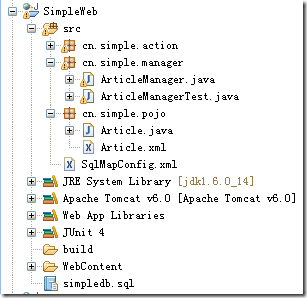
新闻管理的Model层开发完毕,可以供我们的Action调用了,好,Struts 2.1.6 精简实例系列教程,敬请大家期待下文!
本文原创,转载请注明出处,谢谢!http://www.blogjava.net/rongxh7(心梦帆影JavaEE技术博客)
posted on 2009-07-26 03:02
心梦帆影 阅读(3624)
评论(9) 编辑 收藏 所属分类:
Struts2.1.6系列教程