在《SSF入门》中,我曾经提过“虽然Seam针对在JSF里进行数据分页和排序提供了解决方法,但我认为此方法过于简陋,而且不能使用Richfaces的分页控件<rich:datascroller>进行分页。通过SSF数据访问方式,您可以完美结合Richfaces的分页控件简单地实现分页功能。”所以本文旨在给大家演示在SSF中,实现数据分页和排序是如何的方便和快捷。
效果预览
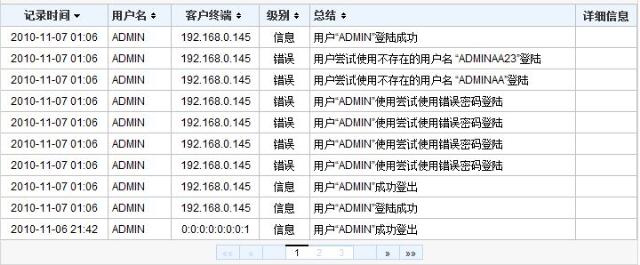
如果大家已经通过上一篇文章正确下载和配置了SSF的话,就已经可以通过菜单“管理->日志”查看分页和排序的效果,如下图所示。可能大家的环境里的日志可能还不足于超过一页的记录(10条),需要增加一些日志记录。要做到这点,只需重复几次登入、登出操作,当然为了使日志更加多样,可以在登入时尝试使用错误的密码或者不存在的用户。
实现原理
首先,我可以看一下日志页面对应的页面逻辑代码(SSF将这些代码称为Action),如下清单所示。
1 package com.whatisjee.ssf.web.action;
2
3 import static com.whatisjee.ssf.web.jsf.FacesUtils.getService;
4
5 import java.io.Serializable;
6
7 import org.jboss.seam.ScopeType;
8 import org.jboss.seam.annotations.Create;
9 import org.jboss.seam.annotations.Name;
10 import org.jboss.seam.annotations.Scope;
11
12 import com.whatisjee.ssf.domain.entity.Log;
13 import com.whatisjee.ssf.domain.service.AppService;
14 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.LogCriteria;
15 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page;
16 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.PagingList;
17 import com.whatisjee.ssf.web.jsf.PagingDataModel;
18
19 @Name("logsAct")
20 @Scope(ScopeType.PAGE)
21 public class LogsAction implements Serializable {
22 private static final long serialVersionUID = -5252797451562495196L;
23
24 private LogCriteria criteria;
25 private PagingDataModel<Log> data;
26 private String detail;
27
28 public LogCriteria getCriteria() {
29 return criteria;
30 }
31
32 public PagingDataModel<Log> getData() {
33 return data;
34 }
35
36 public String getDetail() {
37 return detail;
38 }
39
40 public void setDetail(String detail) {
41 this.detail = detail;
42 }
43
44 @Create
45 public void init() {
46 criteria = new LogCriteria();
47 data = new PagingDataModel<Log>("#{logsAct.find}", false);
48 }
49
50 public PagingList<Log> find(Page page) {
51 AppService service = getService("appService", AppService.class);
52 return service.findLogs(criteria, page);
53 }
54
55 public void find() {
56 data.refresh();
57 }
58
59 public void showDetail() {
60 Log log = (Log) data.getRowData();
61 detail = log.getDetail();
62 }
63 }
如果朋友们有看过我之前的文章《Seam的页面逻辑实现》,应该对上述代码不会陌生,值得注意的是类型分别为LogCriteria和PaginDataModel<Log>的两个域,前者是为了封装界面上传过来的查询条件,后者则是整个数据分页和排序的关键。只需将它绑定到Richfaces的数据列表组件(如<rich:dataTable>、<rich:dataGrid>等),即可实现分页和排序。上例中通过两个参数构造PagingDataModel:第一个字符串参数el用来指明PagingDataModel应该调用那个方法获得数据。它是一个EL表达式,类似#{xxx.xxx}。前半部分的xxx多数情况下与Action的名称相同,在本例中同为“loginAct”。后半部分xxx就是数据获取方法的名称,这个方法必须有且只有一个参数而且类型为com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page,返回值必须为com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.PagingList类型。Page类包含分页和排序必不可少的信息如:从第几行开始获取数据,获取多少行,通过什么列进行排序,升序还是降序等。而PagingList则封装了总共有多少行和本页数据的信息。如本例的find方法通过将LogCriteria和Page传给AppService的findLogs方法,查询数据库获取数据。第二个布尔参数stateful指明PagingDataModel是否需要自己保存状态。如果它是位于有状态的Action中,即Action的Scope为Application、Session、Conversation或者Page,则无需自己保存状态,如本例中应为false。对于那些没有状态的Action,即Scope为Request或Event,应为true。另外,PagingDataModel还有两个可选的构造参数:一个是Page类型指明page首次加载数据时分页信息,另外一个字符串类型id仅用于在stateful为true且在一个页面上有多个PagingDataModel时,将它们区分开来。
至于,详细的PagingDataModel的实现大家如果有兴趣的话,可以过目一下,由于时间有限,我就不做详细解释了。
1 package com.whatisjee.ssf.web.jsf;
2
3 import static com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page.ORDER_ASC;
4 import static com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page.ORDER_DESC;
5 import static org.richfaces.model.Ordering.ASCENDING;
6 import static org.richfaces.model.Ordering.DESCENDING;
7
8 import java.io.IOException;
9 import java.io.Serializable;
10 import java.util.Collection;
11 import java.util.Collections;
12 import java.util.List;
13 import java.util.Map;
14 import java.util.Set;
15
16 import javax.el.ELContext;
17 import javax.el.ELException;
18 import javax.el.ExpressionFactory;
19 import javax.el.MethodExpression;
20 import javax.faces.application.Application;
21 import javax.faces.component.UIViewRoot;
22 import javax.faces.context.FacesContext;
23
24 import org.ajax4jsf.model.DataVisitor;
25 import org.ajax4jsf.model.Range;
26 import org.ajax4jsf.model.SequenceRange;
27 import org.ajax4jsf.model.SerializableDataModel;
28 import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
29 import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
30 import org.richfaces.model.FilterField;
31 import org.richfaces.model.Modifiable;
32 import org.richfaces.model.Ordering;
33 import org.richfaces.model.SortField2;
34
35 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page;
36 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.PagingList;
37 import com.whatisjee.ssf.misc.Page.Order;
38
39 /**
40 * This PagingDataModel is built to support "true" paging and sorting for Richfaces's data iteration components
41 * e.g. <rich:dataTable/>, <rich:dataGrid/>. The "true" paging and sorting means those kinds of things can be
42 * done in database by SQL.
43 * @author Max Yuan(max.m.yuan@gmail.com)
44 * @param <T> A class which must be Serializable.
45 */
46 public class PagingDataModel<T extends Serializable> extends SerializableDataModel implements
47 Modifiable {
48 private static final long serialVersionUID = -5956332259881655981L;
49 private static final Log _LOG = LogFactory.getLog(PagingDataModel.class);
50 private static final String KEY_PAGE = "PAGE";
51 private static final String KEY_LIST = "LIST";
52
53 public static final int DEFAULT_ROWS = 10;
54 public static final String DEFAULT_ID = "DEFAULT";
55
56 private Page page;
57 private PagingList<T> list;
58 private String el;
59 private String keyPage;
60 private String keyList;
61 private boolean stateful;
62
63 private Integer rowKey = new Integer(0);
64 private boolean cached, changed, modified;
65
66 private static Map<String, Object> DUMMY_MAP = new Map<String, Object>() {
67 public void clear() {}
68
69 public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return false; }
70
71 public boolean containsValue(Object value) { return false; }
72
73 public Set<java.util.Map.Entry<String, Object>> entrySet() { return null; }
74
75 public Object get(Object key) { return null; }
76
77 public boolean isEmpty() { return false; }
78
79 public Set<String> keySet() { return null; }
80
81 public Object put(String key, Object value) { return null; }
82
83 public void putAll(Map<? extends String, ? extends Object> m) {}
84
85 public Object remove(Object key) { return null; }
86
87 public int size() { return 0; }
88
89 public Collection<Object> values() { return null; }
90 };
91
92
93 /**
94 * This is construction method to create a PagingDataModel which you can fully control it's behavior.
95 * @param el An EL expression points to a method which must like "public PagingList<T> xxx(Page xxx)".
96 * @param page To specify the total records and initial sorting criteria.
97 * @param id Use to identify this PagingDataModel from another one.
98 * @param stateful Use to specify whether to keep the state to avoid loading data every time page is loaded.
99 * If the Managed Bean who contains this PagingDataModel can keep state, e.g. Session Scope Bean, Application Scope Bean,
100 * Page Scope(only available for Seam) Bean, then this parameter can be "false", otherwise please set it "true".
101 */
102 public PagingDataModel(String el, Page page, String id, boolean stateful) {
103 this.el = el;
104 this.keyPage = KEY_PAGE + "$" + id;
105 this.keyList = KEY_LIST + "$" + id;
106 this.stateful = stateful;
107
108 Map<String, Object> attrs = getAttributes();
109 Object _page = attrs.get(keyPage);
110 if(_page != null) {
111 this.page = (Page) _page;
112 cached = true;
113 } else {
114 this.page = page;
115 attrs.put(keyPage, page);
116 }
117 }
118
119 /**
120 * This construction method create a PagingDataModel with default amount of rows is 10.
121 * @param el An EL expression points to a method which must like "public PagingList<T> xxx(Page xxx)".
122 * @param id Use to identify this PagingDataModel from another one.
123 * @param stateful Use to specify whether to keep the state to avoid loading data every time page is loaded.
124 * If the Managed Bean which contains this PagingDataModel can keep state, e.g. Session Scope Bean, Application Scope Bean,
125 * Page Scope(only available for Seam) Bean, then this parameter can be "false", otherwise please set it "true".
126 */
127 public PagingDataModel(String el, String id, boolean stateful) {
128 this(el, new Page(0, DEFAULT_ROWS), id, stateful);
129 }
130
131 /**
132 * This construction method create a PagingDataModel with default amount of rows is 10 and the id set to be "DEFAULT"
133 * for only one PagingDataModel in a page.
134 * @param el An EL expression points to a method which must like "public PagingList<T> xxx(Page xxx)".
135 * @param stateful Use to specify whether to keep the state to avoid loading data every time page is loaded.
136 * If the Managed Bean which contains this PagingDataModel can keep state, e.g. Session Scope Bean, Application Scope Bean,
137 * Page Scope(only available for Seam) Bean, then this parameter can be "false", otherwise please set it "true".
138 */
139 public PagingDataModel(String el, boolean stateful) {
140 this(el, new Page(0, DEFAULT_ROWS), DEFAULT_ID, stateful);
141 }
142
143 /**
144 * This construction method create a PagingDataModel with default amount of rows is 10 and can keep state.
145 * @param el An EL expression points to a method which must like "public PagingList<T> xxx(Page xxx)".
146 * @param id Use to identify this PagingDataModel from another one.
147 */
148 public PagingDataModel(String el, String id) {
149 this(el, new Page(0, DEFAULT_ROWS), id, true);
150 }
151
152 /**
153 * This construction method create a PagingDataModel with default amount of rows is 10, can keep state and
154 * the id parameter set to be "DEFAULT" for only one PagingDataModel in a page.
155 * @param el An EL expression points to a method which must like "public PagingList<T> xxx(Page xxx)".
156 */
157 public PagingDataModel(String el) {
158 this(el, new Page(0, DEFAULT_ROWS), DEFAULT_ID, true);
159 }
160
161 @Override
162 public void update() {
163 // DO NOTHING
164 }
165
166 @Override
167 public Object getRowKey() {
168 return rowKey;
169 }
170
171 @Override
172 public void setRowKey(Object rowKey) {
173 this.rowKey = (Integer) rowKey;
174 }
175
176 private Map<String, Object> getAttributes() {
177 Map<String, Object> attrs = null;
178 if(stateful){
179 UIViewRoot root = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getViewRoot();
180 attrs = root.getAttributes();
181 } else {
182 attrs = DUMMY_MAP;
183 }
184 return attrs;
185 }
186
187 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
188 private PagingList<T> getList() {
189 if(changed) {
190 refresh();
191 } else if(stateful) {
192 list = (PagingList<T>) getAttributes().get(keyList);
193 }
194 return list;
195 }
196
197 @Override
198 public void walk(FacesContext context, DataVisitor visitor, Range range,
199 Object argument) throws IOException {
200 SequenceRange seqRange = (SequenceRange) range;
201 boolean isNew = page.getFirstRow() != seqRange.getFirstRow();
202 if (isNew) {
203 page.setFirstRow(seqRange.getFirstRow());
204 }
205 page.setRows(seqRange.getRows());
206
207 if(!cached || isNew || modified) {
208 changed = true;
209 modified = false;
210 cached = true;
211 }
212
213 int i = 0;
214 List<T> data = getList().getData();
215 if (data != null) {
216 for (@SuppressWarnings("unused") T t : data) {
217 visitor.process(context, i++, argument);
218 }
219 }
220 }
221
222 @Override
223 public int getRowCount() {
224 PagingList<T> list = getList();
225 return (list == null) ? 0 : list.getCount();
226 }
227
228 @Override
229 public Object getRowData() {
230 PagingList<T> list = getList();
231 return (list == null || list.getData() == null || rowKey == null) ? null
232 : list.getData().get(rowKey.intValue());
233 }
234
235 @Override
236 public int getRowIndex() {
237 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
238 }
239
240 @Override
241 public Object getWrappedData() {
242 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
243 }
244
245 @Override
246 public boolean isRowAvailable() {
247 PagingList<T> list = getList();
248 return (list != null) && (list.getData() != null) && (rowKey != null)
249 && (rowKey.intValue() < list.getData().size());
250 }
251
252 @Override
253 public void setRowIndex(int arg0) {
254 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
255 }
256
257 @Override
258 public void setWrappedData(Object arg0) {
259 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
260 }
261
262 /**
263 * Use to execute the <i>el</i> method to refresh data manually.
264 */
265 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
266 public void refresh() {
267 list = (PagingList<T>) evaluateEL(el, PagingList.class,
268 new Class<?>[] { Page.class }, page);
269 if(list == null) {
270 list = PagingList.EMPTY_LIST;
271 }
272 getAttributes().put(keyList, list);
273 changed = false;
274 }
275
276 private static Object evaluateEL(String el, Class<?> returnType,
277 Class<?>[] paramTypes, Object params) {
params) {
278 Object result = null;
279 FacesContext fc = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance();
280 ELContext elc = fc.getELContext();
281 Application app = fc.getApplication();
282 ExpressionFactory ef = app.getExpressionFactory();
283 MethodExpression me = ef.createMethodExpression(elc, el, returnType, paramTypes);
284 try {
285 result = me.invoke(elc, params);
286 } catch (ELException e) {
287 Throwable cause = e.getCause();
288 if(cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
289 throw ((RuntimeException) cause);
290 } else {
291 if(_LOG.isErrorEnabled()) {
292 _LOG.error("Exception occured during evaluation of EL, because ", cause);
293 }
294 }
295 }
296 return result;
297 }
298
299 @Override
300 public SerializableDataModel getSerializableModel(Range range) {
301 return this;
302 }
303
304 public Page getPage() {
305 return page;
306 }
307
308 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
309 public List<T> getData() {
310 PagingList<T> list = getList();
311 return list != null ? list.getData() : Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
312 }
313
314 public void modify(List<FilterField> filterFields,
315 List<SortField2> sortFields) {
316 if(sortFields != null && sortFields.size() > 0) {
317 SortField2 sf = sortFields.iterator().next();
318
319 String prop = sf.getExpression().getExpressionString();
320 String orderBy = prop.substring(2, prop.length() - 1);
321 if(!orderBy.equals(page.getOrderBy())) {
322 page.setOrderBy(orderBy);
323 modified = true;
324 }
325
326 Ordering ordering = sf.getOrdering();
327 Order order = page.getOrder();
328 if(ASCENDING.equals(ordering) && !ORDER_ASC.equals(order)) {
329 page.setOrder(ORDER_ASC);
330 modified = true;
331 } else if(DESCENDING.equals(ordering) && !ORDER_DESC.equals(order)) {
332 page.setOrder(ORDER_DESC);
333 modified = true;
334 }
335 }
336 }
337
338 }
再来看看页面的XHTML代码片段,如下列表所示。
1 <rich:dataTable id="dtLogs" value="#{logsAct.data}" var="_log" rows="#{logsAct.data.page.rows}" styleClass="list">
2 <rich:column sortBy="#{loggedAt}" styleClass="align-c" headerClass="align-c" selfSorted="true" sortOrder="DESCENDING">
3 <f:facet name="header">
4 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.loggedAt']}"/>
5 </f:facet>
6 <h:outputText value="#{_log.loggedAt}">
7 <s:convertDateTime pattern="#{messages['cmm.shortDateTime']}" />
8 </h:outputText>
9 </rich:column>
10 <rich:column sortBy="#{username}" styleClass="align-l" headerClass="align-l">
11 <f:facet name="header">
12 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.username']}"/>
13 </f:facet>
14 <h:outputText value="#{_log.username}" />
15 </rich:column>
16 <rich:column sortBy="#{terminal}" styleClass="align-c" headerClass="align-c">
17 <f:facet name="header">
18 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.terminal']}"/>
19 </f:facet>
20 <h:outputText value="#{_log.terminal}" />
21 </rich:column>
22 <rich:column sortBy="#{severity}" styleClass="align-c" headerClass="align-c">
23 <f:facet name="header">
24 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.severity']}"/>
25 </f:facet>
26 <h:outputText value="#{messages[$c['LOG_LABELS'][_log.severity - 1][1]]}" />
27 </rich:column>
28 <rich:column sortBy="#{summary}" styleClass="align-l" headerClass="align-l">
29 <f:facet name="header">
30 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.summary']}"/>
31 </f:facet>
32 <h:outputText value="#{sf:getLogSummary(_log)}" />
33 </rich:column>
34 <rich:column styleClass="align-c" headerClass="align-c">
35 <f:facet name="header">
36 <h:outputText value="#{messages['log.detail']}"/>
37 </f:facet>
38 <a4j:commandLink action="#{logsAct.showDetail}" reRender="itDetail" oncomplete="Richfaces.showModalPanel('mpDetail')" rendered="#{not empty _log.detail}" styleClass="icon">
39 <h:graphicImage value="/common/image/view.gif" alt="#{messages['cmm.remove']}" />
40 </a4j:commandLink>
41 </rich:column>
42 </rich:dataTable>
43 <rich:datascroller for="dtLogs" />
这里也有几点需要注意:<rich:dataTable>的rows应该如本例所示,直接使用PagingDataModel里的page的rows域,以免产生不一至。另外,<rich:column>的sortBy属性应为“#{xxx}”的形式,通常为数据库表的列名或Hiberante的实体的域名称。
小结
本文简单地描述了SSF针对SEAM和JSF里的数据分页和排序问题的解决方法。只要大家在项目用到Racefaces,相信上述有代码都会有所帮助。
posted on 2011-01-04 01:10
Max 阅读(4556)
评论(2) 编辑 收藏 所属分类:
Seam系列