几乎所有的Java 集成开发环境都需要调用外部进程进行Java程序的构建,编译,运行和调试,Eclipse,NetBeans,JBuilder和Intellij IDLE概莫例外。在执行过程中,将提示信息以黑色全部打印在控制台里,将异常和错误以红色方式打印。以非常醒目交互体验让程序员远离枯燥和乏味。
现在让我们以Eclipse为例来看看它如何工作的,以揭开它神秘面纱,探究隐藏在后面的秘密。
上篇主要介绍了JAVA IDE Console通过采用Runtime.getRuntime.exec()执行外部程序后,将返回一个Process对象. Process对象能返回三个流:
getInputStream(),对应Process程序的标准输出流。
getErrorStream(), 对应Process程序的标准错误输出流。
getOutputStream();对应Process程序的标准输入流。
函数名之所以与Process程序的方向相反,原因是站在Java Host程序的角度讲的。
现在我们应用此原理来仿真IDE 执行外部程序的过程。
列表1:ConsoleSimulator.java
package
helloworld;
import
java.io.BufferedReader;
import
java.io.IOException;
import
java.io.InputStream;
import
java.io.InputStreamReader;
import
java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* Class for console simulation
*
*
@author
lewhwa
*/
public
class
ConsoleSimulator
implements
Runnable {
private
volatile
boolean
isStop
=
false
;
private
static
final
int
INFO
=
0
;
private
static
final
int
ERROR
=
1
;
private
InputStream is;
private
int
type;
/**
Creates a new instance of StreamInterceptor
*/
public
ConsoleSimulator(InputStream is,
int
type) {
this
.is
=
is;
this
.type
=
type;
}
public
void
run() {
InputStreamReader isr
=
new
InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader reader
=
new
BufferedReader(isr);
String s;
try
{
while
((
!
isStop)
&&
(s
=
reader.readLine())
!=
null
) {
if
(s.length()
!=
0
) {
if
(type
==
INFO) {
System.out.println(
"
INFO>
"
+
s);
}
else
{
System.err.println(
"
ERROR>
"
+
s);
}
try
{
Thread.sleep(
10
);
}
catch
(InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
catch
(IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public
void
stop() {
isStop
=
true
;
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
IOException,
InterruptedException {
//
Process child = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("run.bat");
Process child
=
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(
"
java -classpath bin helloworld.Test
"
);
OutputStream os
=
child.getOutputStream();
InputStream stdin
=
child.getInputStream();
//
InputStream stderr
=
child.getErrorStream();
Thread tIn
=
new
Thread(
new
ConsoleSimulator(stdin, INFO));
Thread tErr
=
new
Thread(
new
ConsoleSimulator(stderr, ERROR));
tIn.start();
tErr.start();
int
result
=
child.waitFor();
tIn.join();
tErr.join();
if
(result
==
0
) {
System.out.println(
"
SUCCESS!
"
);
}
else
{
System.out.println(
"
FAILED!
"
);
}
}
}
外部Bat文件:
列表2
time
/
t
cmd.exe
/
C
/
Q copy
javac
cmd.exe
/
C tree
rem c:\Designer_v5.
1
.0_win32_x86.exe c:\Designer_v5.
1
.0_win32_x861.exe
time
/
t
测试Java类Test.java
列表3:
package helloworld;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**Test Class
* @author lewhwa
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fir = new FileReader("src/helloworld/Test1.java");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fir);
String s;
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
fir.close();
}
}
当ConsoleSimulator程序执行外部的run.bat时,输出如图1所示:

图1
当ConsoleSimulator程序执行外部的java test正常时,输出如图2所示:
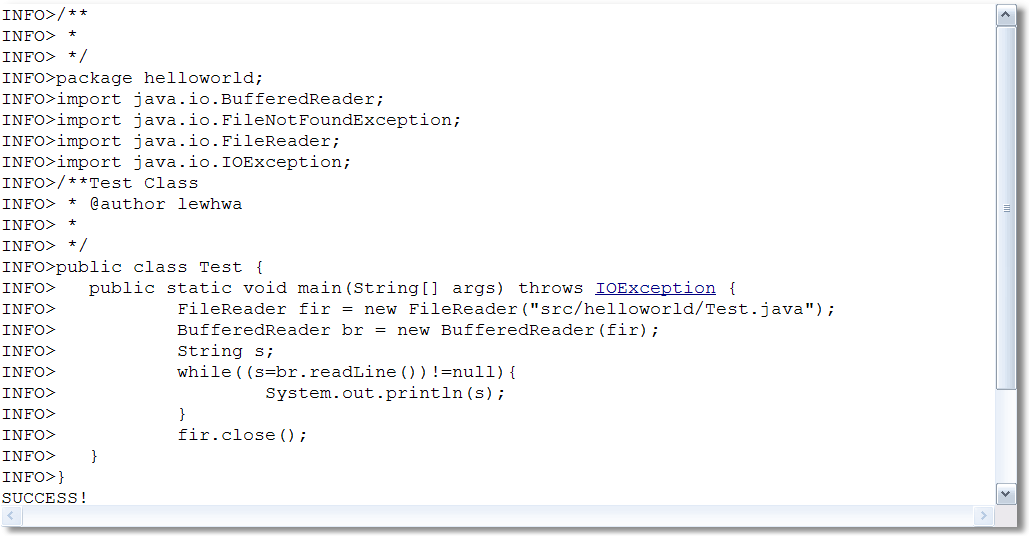
图2
当ConsoleSimulator程序执行外部的java test发生异常时,输出如图3所示:

图3
综上,虽然没有在自己的GUI里将stdout和stderr进行说明,只是用ERROR>提示符和INFO>提示符进行演示,但是完全IDE Console的原理。对ConsoleSimulator稍加修改,完全放入到自己的应用程序当中去。
在我们进行Java程序开发的过程当中,可能涉及到其它的应用程序,借助这种技术,可以很好利用它们,将它们集成到自己的应用当中,将极大地缩短开发周期,何乐而不为呢!